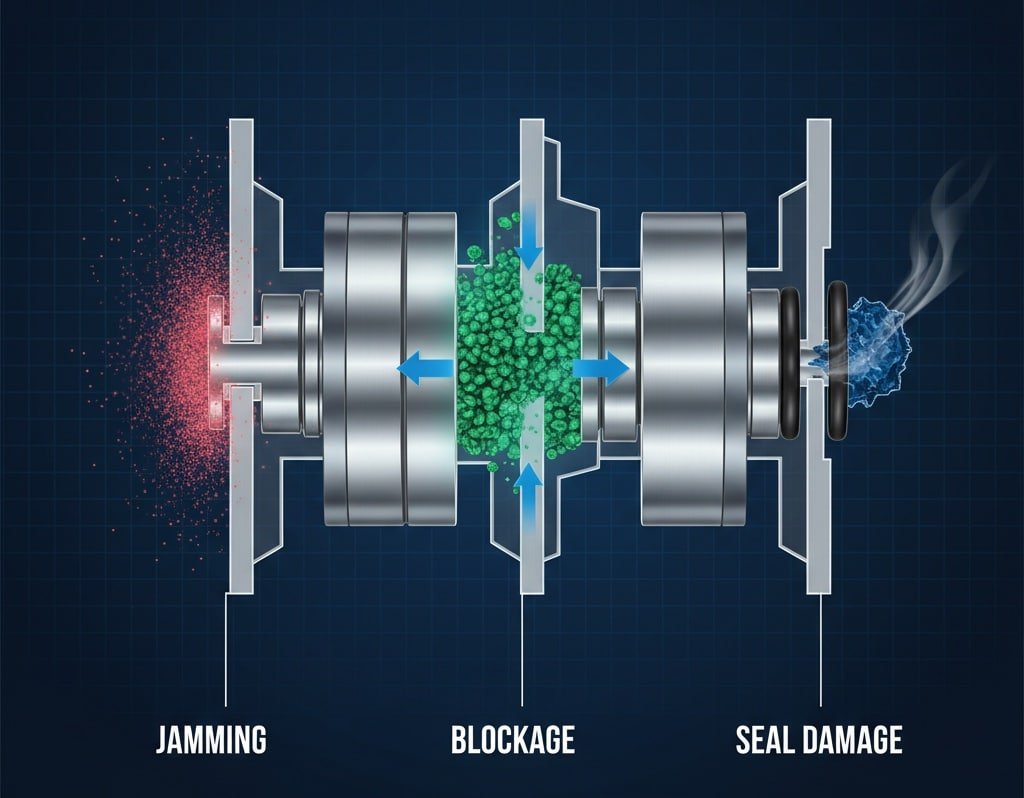
Are microscopic particles destroying your pneumatic valves and causing unexpected system failures? 🔬 Even tiny contaminants as small as 5 microns1 can jam valve mechanisms, erode sealing surfaces, and trigger catastrophic breakdowns that halt production lines. Without proper contamination control, your equipment faces premature wear and costly unplanned downtime.
Το μέγεθος των σωματιδίων της ρύπανσης καθορίζει άμεσα τους τρόπους αστοχίας των βαλβίδων, με τα σωματίδια 5-40 μικρά να προκαλούν εμπλοκή σε βαλβίδες ακριβείας, τα 40-100 μικρά να μπλοκάρουν τις διόδους ροής και τα μεγαλύτερα σωματίδια να προκαλούν βλάβες στις σφραγίδες, απαιτώντας ειδικές στρατηγικές διήθησης για διαφορετικούς τύπους βαλβίδων και εφαρμογές κυλίνδρων χωρίς ράβδο.
Last week, I received an urgent call from David, a maintenance engineer at a pharmaceutical manufacturing plant in Boston, Massachusetts. His precision control valves were failing every few weeks due to microscopic contamination, causing $30,000 daily losses from production stoppages and product quality issues.
Πίνακας περιεχομένων
- How Do Different Micron Sizes Impact Valve Performance?
- Which Valve Types Are Most Susceptible to Contamination Damage?
- What Filtration Strategies Prevent Contamination-Related Failures?
- How Does Contamination Affect Rodless Cylinder Control Systems?
How Do Different Micron Sizes Impact Valve Performance?
Understanding particle size effects helps predict and prevent valve failures. 🎯
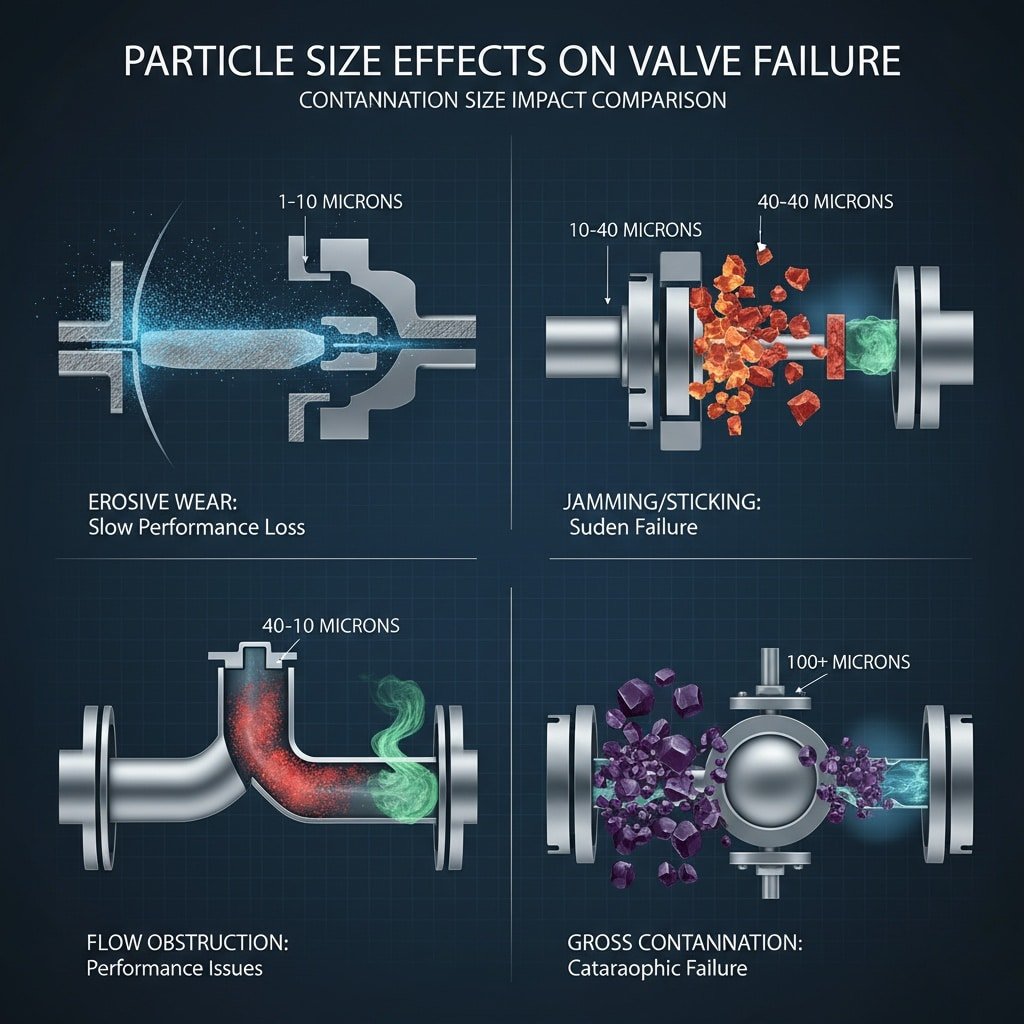
Different contamination sizes cause specific failure modes: 1-10 microns create wear and erosion, 10-40 microns jam moving parts and block orifices, 40-100 microns obstruct flow passages, while particles over 100 microns damage seals and cause gross contamination failures.
Microscopic Contamination (1-10 Microns)
Erosive Wear Mechanisms
Ultra-fine particles act like liquid sandpaper, gradually eroding valve seats, orifices, and sealing surfaces. This contamination size creates the most insidious damage because it’s nearly invisible yet causes progressive performance degradation over time.
Surface Finish Deterioration
- Διάβρωση καθισμάτων: Gradual loss of sealing capability
- Orifice enlargement: Flow rate changes and control issues
- Εξάχνωση επιφάνειας: Αυξημένη τριβή και φθορά
- Coating removal: Loss of protective surface treatments
Fine Contamination (10-40 Microns)
Jamming and Sticking
This size range represents the most critical contamination for precision valves. Particles become trapped in tight clearances, causing valves to stick, jam, or operate erratically.
Critical Clearance Issues
- Spool valves2: 10-25 micron clearances vulnerable to jamming
- Σφαιρικές βαλβίδες: Particles lodge between ball and seat
- Βαλβίδες βελόνας: Fine adjustment mechanisms affected
- Check valves: Spring-loaded mechanisms compromised
Medium Contamination (40-100 Microns)
Flow Obstruction
Larger particles create flow restrictions and pressure drops, affecting system performance and valve response times.
Επιπτώσεις στην απόδοση του συστήματος
- Reduced flow capacity: Partial blockage of passages
- Διακυμάνσεις πίεσης: Unstable system operation
- Response delays: Slower valve actuation
- Ασυνεπής λειτουργία: Variable performance characteristics
Contamination Size Impact Comparison
| Μέγεθος σωματιδίων | Πρωτογενές αποτέλεσμα | Valve Impact | Τρόπος αποτυχίας |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-10 microns | Erosive wear | Σταδιακή υποβάθμιση | Slow performance loss |
| 10-40 μικρά | Jamming/sticking | Immediate malfunction | Sudden failure |
| 40-100 microns | Flow obstruction | Μειωμένη χωρητικότητα | Ζητήματα επιδόσεων |
| 100+ microns | Gross contamination | Multiple damage modes | Καταστροφική αποτυχία |
Detection and Monitoring
Particle Analysis Methods
- Μετρητές σωματιδίων λέιζερ3: Real-time contamination monitoring
- Microscopic analysis: Detailed particle characterization
- Filter analysis: Contamination source identification
- Ανάλυση πετρελαίου: System-wide contamination assessment
Which Valve Types Are Most Susceptible to Contamination Damage?
Different valve designs have varying contamination sensitivity levels. ⚙️
Precision control valves and αναλογικές βαλβίδες4 are most contamination-sensitive due to tight clearances, while ball valves and gate valves offer better contamination tolerance, requiring valve-specific filtration strategies for optimal performance and reliability.
High-Sensitivity Valve Types
Servo and Proportional Valves
These precision valves have extremely tight tolerances and are most vulnerable to contamination damage. Even 5-micron particles can cause significant performance issues.
Critical Specifications
- Clearances: 5-15 microns typical
- Filtration requirement: 3-5 micron absolute
- Sensitivity level: Extremely high
- Failure impact: Immediate performance loss
Βαλβίδες με πιλότο
Small pilot orifices and control passages make these valves highly susceptible to contamination blockage.
Medium-Sensitivity Valve Types
Ηλεκτρομαγνητικές βαλβίδες
Standard solenoid valves have moderate contamination sensitivity, with 25-40 micron filtration typically sufficient for reliable operation.
Σκέψεις σχεδιασμού
- Orifice sizes: 0.5-2.0mm typical
- Clearances: 25-50 microns
- Filtration requirement: 25-40 μικρά ονομαστικά
- Συχνότητα συντήρησης: Moderate
Low-Sensitivity Valve Types
Ball and Gate Valves
These valve types offer excellent contamination tolerance due to larger clearances and robust sealing mechanisms.
Ανοχή μόλυνσης
- Particle tolerance: Up to 100 microns
- Sealing mechanism: Less sensitive to particles
- Απαιτήσεις συντήρησης: Minimal
- Καταλληλότητα εφαρμογής: Dirty environments
Valve Contamination Sensitivity Ranking
| Τύπος βαλβίδας | Sensitivity Level | Critical Particle Size | Required Filtration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Servo/Proportional | Extremely High | 5 μικρά | 3-5 micron absolute |
| Πιλοτική λειτουργία | Πολύ υψηλή | 10 microns | 10 micron absolute |
| Standard solenoid | Μεσαίο | 25 microns | 25 micron nominal |
| Ball/Gate valves | Χαμηλή | 100 microns | 40 micron nominal |
Εφαρμογή σε πραγματικό κόσμο
Consider the experience of Jennifer, a process engineer at an automotive assembly plant in Detroit, Michigan. Her precision positioning system using servo valves was experiencing frequent failures due to 15-micron metal particles from machining operations. We provided a complete Bepto filtration and valve replacement package with 5-micron absolute filtration, eliminating contamination failures and reducing maintenance costs by 45%. 💪
What Filtration Strategies Prevent Contamination-Related Failures?
Proper filtration design prevents contamination damage and extends valve life. 🛡️
Effective contamination control requires multi-stage filtration with 10:1 safety factors, combining coarse pre-filters, fine main filters, and point-of-use filters matched to valve sensitivity levels, plus regular filter maintenance and contamination monitoring programs.
Multi-Stage Filtration Design
Primary Filtration (Coarse)
Remove large particles and debris before they reach sensitive components.
Filtration Stages
- Intake filters: 100-200 micron screens
- Tank breathers: Prevent atmospheric contamination
- Suction strainers: Protect pumps and compressors
- Return filters: Clean fluid returning to reservoir
Secondary Filtration (Fine)
Provide precise contamination control for sensitive valve applications.
Fine Filter Selection
- Absolute vs. nominal: Choose appropriate rating type
- Beta ratios5: Understand filter efficiency ratings
- Χωρητικότητα ροής: Match filter size to system requirements
- Bypass protection: Prevent unfiltered flow during overload
Valve-Specific Filtration Requirements
Εφαρμογές υψηλής ακρίβειας
Servo valves and proportional valves require the finest filtration levels.
Critical Filter Specifications
- Filtration level: 3-5 micron absolute
- Αναλογία βήτα: β5 ≥ 1000 (99.9% efficiency)
- Τοποθεσία: Point-of-use installation
- Εφεδρεία: Backup filtration systems
Τυπικές εφαρμογές
Most pneumatic valves operate reliably with moderate filtration levels.
Bepto Filtration Solutions
| Εφαρμογή | Προσέγγιση OEM | Πλεονέκτημα Bepto | Εξοικονόμηση κόστους |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-precision | Expensive proprietary filters | Compatible alternatives | 35-45% |
| Τυπικό καθήκον | Περιορισμένες επιλογές | Comprehensive range | 25-35% |
| Συντήρηση | Complex procedures | Simplified systems | 40-50% |
| Παρακολούθηση | Separate equipment | Integrated solutions | 30-40% |
Contamination Monitoring
Συστήματα συνεχούς παρακολούθησης
- Online particle counters: Real-time contamination levels
- Διαφορά πίεσης: Filter condition monitoring
- Οπτικοί δείκτες: Simple contamination alerts
- Καταγραφή δεδομένων: Track contamination trends
Προληπτική συντήρηση
- Filter replacement schedules: Based on contamination levels
- System flushing: Remove accumulated contamination
- Επιθεώρηση εξαρτημάτων: Check for contamination damage
- Fluid analysis: Monitor system cleanliness
How Does Contamination Affect Rodless Cylinder Control Systems?
Rodless cylinders require exceptional contamination control for precise operation. 🎯
Contamination in rodless cylinder systems causes positioning errors, seal wear, and guide rail damage, requiring 10-25 micron filtration for standard applications and 5-10 micron filtration for precision positioning, with special attention to control valve contamination sensitivity.
System-Specific Contamination Issues
Επίδραση της ακρίβειας εντοπισμού θέσης
Contamination affects the precision control valves that govern rodless cylinder movement, causing positioning errors and repeatability issues.
Critical Control Elements
- Σερβοβαλβίδες: Require 5-micron absolute filtration
- Βαλβίδες ελέγχου ροής: Need 25-micron nominal filtration
- Ρυθμιστές πίεσης: Sensitive to 40-micron contamination
- Feedback sensors: Affected by system contamination
Seal and Guide System Protection
Linear Guide Contamination
Particles accumulate on guide rails and bearing surfaces, causing increased friction and premature wear.
Στρατηγικές προστασίας
- Bellows covers: Protect guide rails from contamination
- Σφραγίδες υαλοκαθαριστήρων: Remove particles from rod surfaces
- Filtered air supply: Clean pneumatic media
- Τακτικός καθαρισμός: Maintenance procedures
Integrated Contamination Control
System Design Approach
Our Bepto rodless cylinder systems include comprehensive contamination control designed specifically for precision applications.
Complete Protection Package
- Matched filtration: Valve-specific filter selection
- Ενσωμάτωση συστήματος: Coordinated contamination control
- Monitoring capability: Real-time cleanliness assessment
- Maintenance support: Expert technical guidance
Βελτιστοποίηση επιδόσεων
Παράδειγμα εφαρμογής
Take the success story of Mark, a production manager at a semiconductor equipment manufacturer in San Jose, California. His rodless cylinder positioning system was experiencing 50-micron positioning errors due to contamination in the control valves. We implemented a complete Bepto contamination control system with 5-micron filtration, achieving ±5-micron positioning accuracy and eliminating contamination-related downtime. 🚀
Ανάλυση κόστους-οφέλους
- Filtration investment: $2,000 system upgrade
- Downtime reduction: 95% fewer contamination failures
- Εξοικονόμηση πόρων συντήρησης: 60% reduction in service calls
- Βελτίωση της ποιότητας: 10x better positioning accuracy
Proper contamination control ensures reliable rodless cylinder operation, prevents costly failures, and maintains precision performance across demanding industrial applications.
FAQs About Contamination Control
What particle size causes the most valve damage?
Particles in the 10-40 micron range cause the most immediate valve damage by jamming in critical clearances and blocking small orifices. This size range is particularly problematic because particles are large enough to bridge clearances but small enough to penetrate deep into valve mechanisms. Our Bepto filtration systems specifically target this critical contamination size.
How often should filters be changed in contaminated environments?
Filter change intervals depend on contamination levels but typically range from 500-2000 operating hours, with pressure differential monitoring providing the most accurate replacement timing. Heavily contaminated environments may require monthly changes, while clean systems can operate 6-12 months between changes. We provide contamination monitoring equipment to optimize change intervals.
Can contamination damage be repaired or must valves be replaced?
Minor contamination damage like surface erosion can often be repaired through reconditioning, but severe jamming or seal damage typically requires valve replacement. Early detection through contamination monitoring allows repair before catastrophic failure occurs. Our Beipo replacement valves offer cost-effective alternatives to expensive OEM repairs.
What’s the difference between absolute and nominal filtration ratings?
Absolute ratings guarantee removal of all particles above the specified size, while nominal ratings indicate the size at which 50% of particles are removed. For critical applications, absolute ratings provide better protection. Absolute 10-micron filters remove 99.9% of particles 10 microns and larger, while nominal 10-micron filters remove only 50% of 10-micron particles.
How do I determine the right filtration level for my application?
Select filtration levels based on the most sensitive component in your system, typically 5-10 times finer than the critical clearance dimension. Servo valves need 3-5 micron absolute, standard solenoids need 25 micron nominal, and ball valves can use 40 micron nominal. Our technical team provides free contamination analysis and filtration recommendations for your specific application.
-
Learn exactly how small a micron (micrometer) is and see visual comparisons. ↩
-
See an animation of how spool valves function to direct airflow in pneumatic systems. ↩
-
See the operating principles behind laser particle counters for measuring contamination. ↩
-
Get a clear definition of proportional valves and their function in flow control systems. ↩
-
Learn how Beta ratios are calculated and what they mean for a filter’s performance and efficiency. ↩





