Are you struggling with space constraints in your automation systems? Traditional cylinders often require twice their stroke length in installation space, causing design headaches and inefficiency. Rodless pneumatic cylinders1 offer a compact yet powerful solution.
Rodless cylinders provide linear motion in a space-saving design by containing the piston and carriage in the same profile, eliminating the need for an external rod while delivering the same force and precision as conventional cylinders.
I remember visiting a manufacturing plant in Germany last year where the engineer showed me how switching to rodless cylinders reduced their machine footprint by 40% while improving performance. Let me share what I’ve learned from 15+ years in the pneumatic solutions industry.
How Do Rodless Cylinders Enable Precision Positioning in Flexible Display Production?
Flexible display manufacturing2 requires exceptional positioning accuracy and smooth motion control to ensure quality and prevent damage to delicate materials.
Magnetic rodless cylinders excel in flexible display production by providing precise, vibration-free movement with positioning accuracy of ±0.05mm, while their compact design allows for integration into tight spaces where traditional cylinders cannot fit.
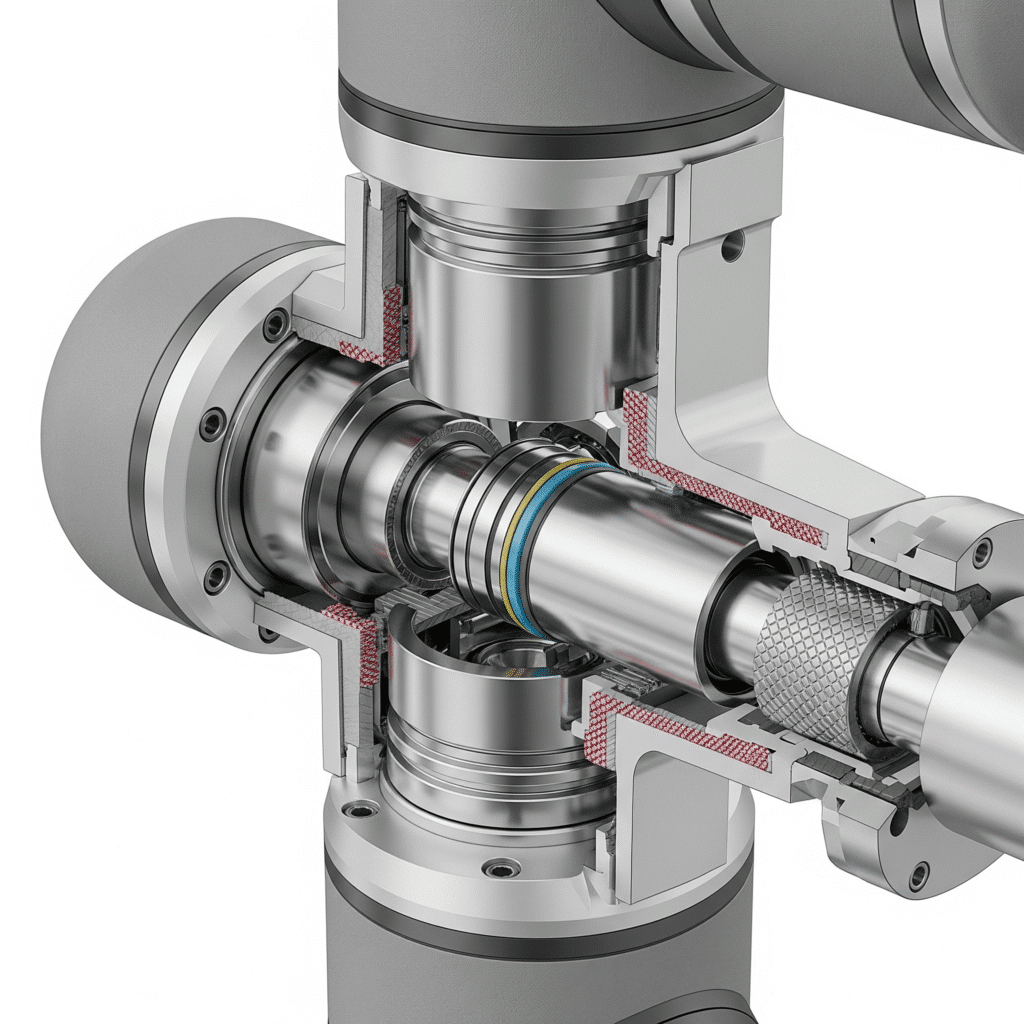
Key Benefits for Display Manufacturing
Rodless cylinders offer several advantages in this demanding application:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Low-friction seals | Smooth, stick-slip free motion |
| Integrated position sensors | Real-time position feedback |
| Compact profile | Space-saving in clean room environments |
| Adjustable cushioning | Protection for sensitive components |
Case Study: OLED Production Efficiency
One of our customers in South Korea was experiencing inconsistent quality in their OLED panel production. Their traditional cylinder-based positioning system created vibration issues affecting panel alignment.
After implementing our guided rodless cylinder solution with integrated position feedback, they achieved:
- 30% reduction in positioning errors
- 25% increase in production throughput
- Significant decrease in panel rejection rates
How Can Rodless Cylinders Improve Semiconductor Wafer Handling?
Semiconductor wafer handling3 requires contamination-free environments and gentle handling of extremely valuable silicon wafers during processing steps.
Double-acting rodless cylinders with vacuum suction capabilities provide ideal wafer handling solutions by combining smooth linear motion with integrated vacuum channels, eliminating the need for external tubing that could introduce particles or cause wafer damage.
Vacuum Integration Advantages
Modern rodless cylinders can be configured with:
- Internal vacuum channels
- Multi-circuit vacuum zones
- Integrated venturi generators
- Leak detection systems
This integration reduces the complexity of wafer handling systems while improving reliability. The enclosed design also prevents contamination from entering the clean room environment.
What Makes Rodless Cylinders Ideal for SMT Z-axis Actuation?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT)4 equipment requires precise vertical movement for component placement, with accuracy requirements in the micron range.
Electric rodless cylinders provide the ideal Z-axis actuation for SMT equipment with their programmable motion profiles, high repeatability (±0.01mm), and compact form factor that allows for multiple placement heads in limited space.

Precision Control Features
When implementing rodless cylinders in SMT applications, these features are critical:
- Servo-controlled motion for variable speed and acceleration
- Absolute position encoding for instant homing
- Zero-backlash drive mechanisms
- Rigid carriage design to resist deflection under load
I recently worked with a European electronics manufacturer who reduced their pick-and-place cycle time by 18% after upgrading to our high-speed rodless cylinder solution, resulting in significant productivity gains.
How Do Rodless Cylinders Enhance CNC Tool Changer Systems?
CNC machining centers require rapid tool changes to minimize non-productive time, with reliability being paramount to prevent costly downtime.
Pneumatic rodless cylinders excel in CNC tool changer applications by providing fast, reliable linear motion in a compact package, with speeds up to 3m/s and cycle life exceeding 10 million operations—essential for high-volume production environments.
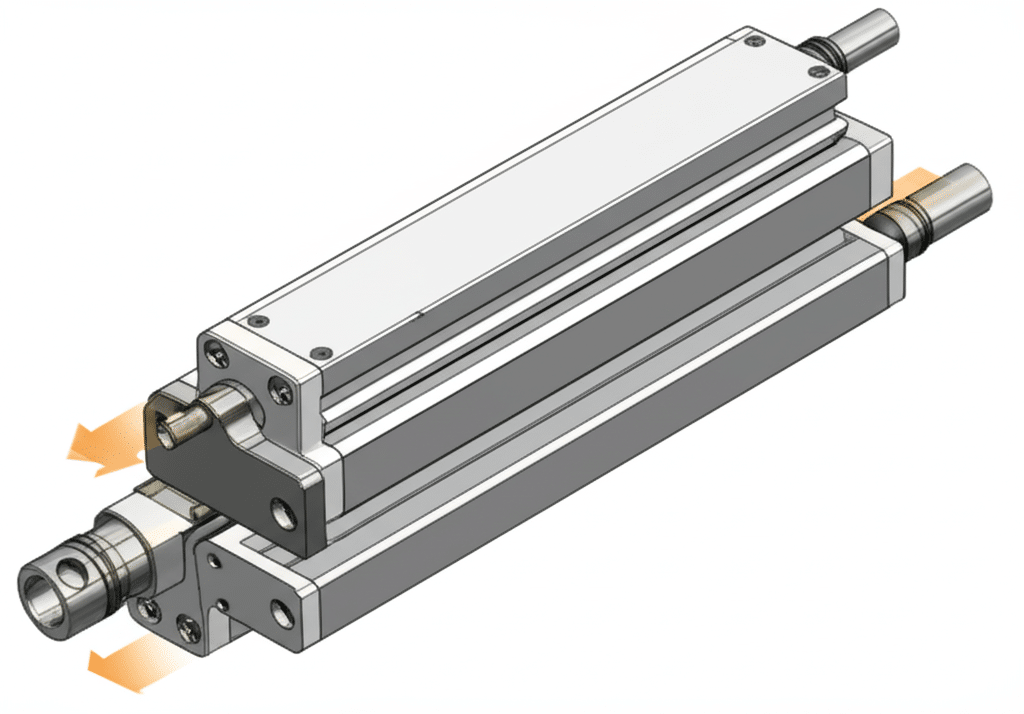
Optimizing Tool Change Operations
Key Performance Metrics
| Parameter | Typical Value | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Max Speed | 3 m/s | Reduces tool change time |
| Acceleration | Up to 30 m/s² | Minimizes cycle time |
| Cycle Life | >10 million | Reduces maintenance |
| Load Capacity | Up to 500 kg | Handles heavy tooling |
What Role Do Rodless Cylinders Play in Cobot Joint Space Optimization?
Collaborative robots (cobots)5 require compact actuation systems that maintain human-safe operation while delivering precise movement.
Guided rodless cylinders provide an ideal solution for cobot joint mechanisms by offering a high force-to-size ratio, integrated position feedback, and adjustable cushioning that ensures smooth motion profiles essential for human-robot collaboration.
Safety and Performance Balance
When designing cobots with rodless cylinders, these factors are critical:
- Low-inertia carriage designs
- Programmable deceleration profiles
- Force-limiting capabilities
- Enclosed moving parts
Application Example: Assembly Line Integration
By implementing magnetic rodless cylinders in cobot arm extensions, manufacturers can achieve:
- Extended reach without compromising precision
- Reduced overall robot weight
- Simplified maintenance compared to complex joint mechanisms
- Enhanced safety through controlled force application
Conclusion
Rodless pneumatic cylinders offer game-changing benefits across industrial automation applications, from display manufacturing to collaborative robotics. Their space-saving design, precision, and reliability make them an ideal choice for engineers facing increasingly complex automation challenges.
FAQs About Rodless Cylinders
What is a rodless pneumatic cylinder?
A rodless pneumatic cylinder is a linear actuator that contains its piston and carriage within the same profile, eliminating the external rod found in conventional cylinders while providing the same force and motion capabilities in a more compact package.
How does a rodless air cylinder work?
Rodless air cylinders work by using compressed air to move a piston inside a sealed tube. The piston is mechanically connected to an external carriage through a slot in the cylinder body, which is sealed by various mechanisms (magnetic coupling, mechanical seals, or bands) to prevent air leakage.
What are the main applications for rodless cylinders?
Rodless cylinders excel in applications requiring long strokes in limited spaces, including material handling, packaging machinery, automation systems, semiconductor equipment, and robotics. Their compact design makes them ideal for space-constrained environments.
How do magnetic rodless cylinders differ from mechanical types?
Magnetic rodless cylinders use magnetic coupling between the internal piston and external carriage, eliminating the need for mechanical connections through the cylinder wall. This design offers leak-free operation and reduced friction, though typically with lower force capabilities than mechanical designs.
What maintenance do rodless cylinders require?
Rodless cylinders require periodic inspection of seals, lubrication of guide systems (if applicable), and cleaning of external surfaces. Magnetic types generally require less maintenance than mechanical band or slider types due to fewer wearing components.
-
Learn more about the fundamental mechanics and types of rodless pneumatic cylinders, and how they differ from traditional cylinders. ↩
-
Understand the complex manufacturing process of flexible displays like OLEDs and the precision required at each step. ↩
-
Discover the critical steps and stringent requirements for handling silicon wafers in a contamination-free semiconductor manufacturing environment. ↩
-
Gain a foundational understanding of Surface Mount Technology (SMT), the leading method for assembling modern electronic circuits. ↩
-
Explore the definition, safety features, and applications of collaborative robots (cobots) and how they work alongside humans in various industries. ↩



