Production managers struggle with space constraints daily. Traditional actuators don’t fit in modern compact machinery. Engineers need solutions that deliver power without consuming excessive space.
Rodless cylinders are used in packaging machinery, automotive assembly lines, material handling systems, conveyor applications, pick-and-place equipment, and manufacturing processes where space limitations, long strokes, or safety concerns make traditional rod cylinders impractical.
Yesterday, I received a call from Maria, a plant engineer at a Spanish food processing facility. Their new packaging line needed 1.5-meter stroke actuators but had only 2 meters of available space. Traditional cylinders would need 3.5 meters. We provided magnetic rodless cylinders that fit perfectly and increased their packaging speed by 40%.
Table of Contents
- What Industries Rely Most Heavily on Rodless Cylinders?
- Which Manufacturing Applications Benefit from Rodless Cylinder Technology?
- How Are Rodless Cylinders Used in Packaging and Material Handling?
- What Automotive Applications Use Rodless Cylinders?
- Where Do You Find Rodless Cylinders in Food and Pharmaceutical Industries?
- How Are Rodless Cylinders Applied in Specialized Industrial Equipment?
- Conclusion
- FAQs About Rodless Cylinder Applications
What Industries Rely Most Heavily on Rodless Cylinders?
Different industries adopt rodless cylinders for specific advantages. I work with customers across multiple sectors to solve space and performance challenges. Understanding industry needs helps select the right solutions.
Industries that rely heavily on rodless cylinders include automotive manufacturing, packaging and food processing, pharmaceutical production, electronics assembly, textile machinery, and material handling systems where space efficiency and long stroke capabilities are critical.
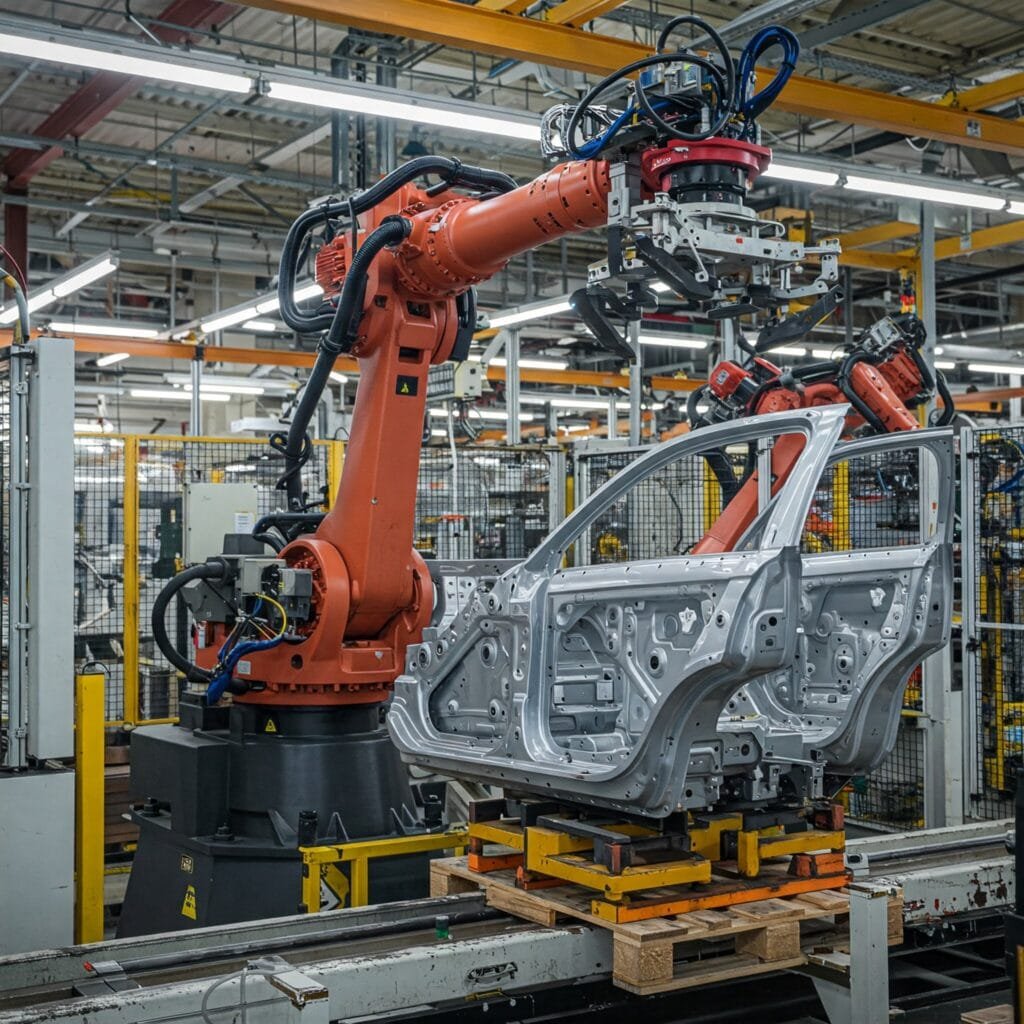

Automotive Manufacturing Industry
Automotive assembly lines use rodless cylinders extensively for welding fixtures, part positioning, and transfer systems. Space constraints in modern factories make rodless designs essential.
Body-in-white1 assembly stations use guided rodless cylinders to position car bodies for welding. These systems handle heavy loads while maintaining precise positioning. Stroke lengths often exceed 2 meters for full vehicle positioning.
Paint booth conveyors rely on rodless cylinders for smooth, contamination-free operation. Magnetic coupling prevents paint particles from entering the cylinder, maintaining clean operation in harsh environments.
Engine assembly lines use compact rodless cylinders for component insertion and testing. The space savings allow more operations in smaller areas, improving production efficiency.
Packaging and Converting Industry
Packaging machinery represents the largest application area for rodless cylinders. High-speed operations and compact machine designs drive adoption across all packaging types.
Horizontal form-fill-seal2 machines use rodless cylinders for film feeding and product positioning. Long stroke capabilities handle various package sizes without machine modifications.
Cartoning equipment relies on rodless cylinders for carton forming, loading, and sealing operations. The smooth operation prevents damage to delicate packages.
Labeling machines use precision rodless cylinders for label application and product positioning. Accurate positioning ensures proper label placement at high speeds.
Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
Clean room environments in electronics manufacturing benefit from sealed rodless cylinder designs. Contamination control is critical for product quality.
PCB assembly equipment uses rodless cylinders for component placement and board handling. Precise positioning ensures accurate component placement on circuit boards.
Semiconductor wafer handling systems rely on ultra-clean rodless cylinders. Magnetic coupling prevents particle generation that could contaminate sensitive processes.
Display panel manufacturing uses large rodless cylinders for glass substrate handling. Long strokes accommodate various panel sizes in the same equipment.
Textile and Converting Machinery
Textile machinery uses rodless cylinders for fabric handling, cutting, and processing operations. The smooth operation prevents fabric damage during processing.
Web handling equipment relies on rodless cylinders for tension control and web positioning. Consistent operation maintains product quality throughout the process.
Printing presses use rodless cylinders for paper feeding and registration systems. Precise positioning ensures accurate printing registration.
| Industry Sector | Primary Applications | Typical Stroke Lengths | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Assembly, Welding, Painting | 500-3000mm | Space Savings, Heavy Loads |
| Packaging | Form-Fill-Seal, Cartoning | 200-2000mm | High Speed, Compact Design |
| Electronics | PCB Assembly, Wafer Handling | 100-1000mm | Clean Operation, Precision |
| Textile | Fabric Handling, Web Control | 300-2500mm | Smooth Operation, Reliability |
Material Handling and Logistics
Warehouse automation systems use rodless cylinders for sorting, conveying, and storage applications. E-commerce growth drives demand for automated material handling.
Automated storage and retrieval systems rely on rodless cylinders for precise positioning of storage and retrieval mechanisms. Long stroke capabilities handle various storage configurations.
Conveyor systems use rodless cylinders for diverting, lifting, and positioning operations. The compact design allows integration into existing conveyor layouts.
Palletizing equipment uses heavy-duty rodless cylinders for layer formation and pallet handling. High force capacity handles heavy loads efficiently.
Medical Device Manufacturing
Medical device production requires clean, precise operation that rodless cylinders provide. Regulatory requirements drive adoption of contamination-free designs.
Pharmaceutical packaging uses rodless cylinders for blister pack formation and tablet handling. Clean operation prevents contamination of sterile products.
Medical device assembly relies on precision rodless cylinders for component placement and testing. Accurate positioning ensures product quality and safety.
Which Manufacturing Applications Benefit from Rodless Cylinder Technology?
Specific manufacturing processes gain significant advantages from rodless cylinder technology. I help customers identify applications where rodless cylinders provide the best return on investment.
Manufacturing applications that benefit most from rodless cylinders include long-stroke positioning systems, high-speed assembly operations, space-constrained equipment, clean room processes, and applications requiring precise positioning with heavy load handling.
Assembly Line Operations
Assembly lines use rodless cylinders for part feeding, positioning, and fastening operations. The space savings allow more workstations in the same floor area.
Automated assembly systems rely on rodless cylinders for precise component placement. Position accuracy ensures proper assembly without rework or quality issues.
Multi-station assembly equipment uses rodless cylinders for workpiece transfer between stations. Smooth operation prevents damage to delicate components.
Robotic assembly cells integrate rodless cylinders for tool positioning and part handling. The compact design allows robots to work in smaller spaces.
Machining and Metalworking
CNC machine tools use rodless cylinders for workpiece clamping and positioning. The space savings allow more complex tooling setups in standard machines.
Transfer machines rely on rodless cylinders for part movement between machining stations. Long stroke capabilities handle various part sizes efficiently.
Grinding machines use rodless cylinders for workpiece feeding and positioning. Precise positioning ensures consistent surface finishes.
Press operations use rodless cylinders for part feeding and ejection systems. High force capacity handles heavy stampings and forgings.
Testing and Inspection Equipment
Quality control equipment uses rodless cylinders for sample positioning and testing operations. Precise positioning ensures accurate test results.
Coordinate measuring machines3 rely on rodless cylinders for probe positioning and workpiece handling. The smooth operation prevents measurement errors.
Leak testing equipment uses rodless cylinders for part positioning and sealing. Consistent operation ensures reliable test results.
Vision inspection systems use rodless cylinders for part positioning and camera movement. Precise positioning enables accurate defect detection.
Welding and Joining Operations
Welding fixtures use guided rodless cylinders for workpiece positioning and clamping. The high force capacity handles heavy weldments securely.
Resistance welding equipment relies on rodless cylinders for electrode positioning and pressure application. Consistent pressure ensures reliable weld quality.
Adhesive dispensing systems use rodless cylinders for applicator positioning and substrate handling. Precise positioning ensures accurate adhesive placement.
Ultrasonic welding equipment uses rodless cylinders for part positioning and pressure application. The smooth operation prevents part damage during welding.
How Are Rodless Cylinders Used in Packaging and Material Handling?
Packaging represents the largest application area for rodless cylinders. High-speed operations and space constraints drive widespread adoption across all packaging types.
Rodless cylinders are used in packaging for film feeding, product positioning, carton forming, case packing, palletizing, and conveyor systems where long strokes, high speeds, and compact designs are essential for efficient operation.
Form-Fill-Seal Packaging Machines
Horizontal form-fill-seal machines use rodless cylinders for film feeding and sealing operations. Long stroke capabilities accommodate various package sizes without machine modifications.
Vertical form-fill-seal equipment relies on rodless cylinders for film positioning and product feeding. The compact design allows more operations in smaller machines.
Pouch making machines use rodless cylinders for film handling and sealing operations. Smooth operation prevents film damage and ensures consistent sealing.
Bag making equipment uses rodless cylinders for film feeding, cutting, and sealing. High-speed operation increases production rates significantly.
Cartoning and Case Packing
Cartoning machines use rodless cylinders for carton forming, loading, and sealing operations. The space savings allow more complex cartoning operations in compact machines.
Carton erecting equipment relies on rodless cylinders for carton forming and positioning. Precise positioning ensures proper carton formation without jamming.
Case packing machines use rodless cylinders for product loading and case sealing. High force capacity handles heavy product loads efficiently.
Tray forming equipment uses rodless cylinders for tray erecting and positioning. The smooth operation prevents damage to delicate trays.
Labeling and Coding Systems
Labeling machines use precision rodless cylinders for label application and product positioning. Accurate positioning ensures proper label placement at high speeds.
Print and apply systems rely on rodless cylinders for label positioning and application pressure. Consistent operation ensures reliable label adhesion.
Coding equipment uses rodless cylinders for print head positioning and substrate handling. Precise positioning ensures accurate code placement.
Sleeve labeling machines use rodless cylinders for sleeve positioning and shrink tunnel feeding. Long stroke capabilities handle various container sizes.
Conveyor and Sorting Systems
Conveyor systems use rodless cylinders for diverting, lifting, and positioning operations. The compact design allows integration into existing conveyor layouts.
Sorting equipment relies on rodless cylinders for product diverting and positioning. High-speed operation increases sorting throughput significantly.
Accumulation conveyors use rodless cylinders for product stopping and releasing. Smooth operation prevents product damage during accumulation.
Merge conveyors use rodless cylinders for product timing and positioning. Precise control ensures smooth product flow without collisions.
| Packaging Application | Typical Stroke Length | Speed Requirements | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Form-Fill-Seal | 200-1500mm | High Speed | Space Savings, Reliability |
| Cartoning | 150-800mm | Medium Speed | Precise Positioning, Compact |
| Labeling | 50-300mm | High Speed | Accuracy, Smooth Operation |
| Conveying | 100-2000mm | Variable | Flexibility, Integration |
Palletizing and Depalletizing
Palletizing equipment uses heavy-duty rodless cylinders for layer formation and pallet handling. High force capacity handles heavy loads efficiently.
Layer forming systems rely on rodless cylinders for product positioning and layer compression. Precise positioning ensures stable pallet loads.
Depalletizing equipment uses rodless cylinders for layer lifting and product separation. Smooth operation prevents product damage during depalletizing.
Pallet handling systems use rodless cylinders for pallet positioning and clamping. The long stroke capabilities handle various pallet sizes.
Stretch Wrapping and Strapping
Stretch wrapping machines use rodless cylinders for film carriage positioning and pallet handling. Long stroke capabilities accommodate various load heights.
Strapping equipment relies on rodless cylinders for strap feeding and tensioning. Precise positioning ensures consistent strap placement.
Shrink wrapping machines use rodless cylinders for film positioning and sealing operations. Smooth operation prevents film damage during wrapping.
Banding equipment uses rodless cylinders for band positioning and tensioning. High force capacity ensures secure band application.
What Automotive Applications Use Rodless Cylinders?
Automotive manufacturing relies heavily on rodless cylinders for assembly, welding, and handling operations. Space constraints and precision requirements drive widespread adoption.
Automotive applications for rodless cylinders include body-in-white assembly, welding fixtures, paint line conveyors, engine assembly, powertrain manufacturing, and quality testing equipment where space efficiency and precise positioning are critical.
Body-in-White Assembly
Body-in-white assembly stations use guided rodless cylinders to position car bodies for welding operations. These systems handle heavy loads while maintaining precise positioning accuracy.
Welding fixtures rely on rodless cylinders for workpiece clamping and positioning. The high force capacity securely holds body panels during welding operations.
Hemming4 operations use rodless cylinders for panel positioning and forming. Precise positioning ensures consistent hem quality and appearance.
Spot welding equipment uses rodless cylinders for electrode positioning and pressure application. Consistent pressure ensures reliable weld quality.
Paint Shop Operations
Paint booth conveyors rely on rodless cylinders for smooth, contamination-free operation. Magnetic coupling prevents paint particles from entering the cylinder.
Spray booth equipment uses rodless cylinders for part positioning and masking operations. Clean operation prevents contamination of painted surfaces.
Paint line handling systems use rodless cylinders for vehicle positioning and rotation. Long stroke capabilities handle various vehicle sizes.
Oven conveyor systems rely on rodless cylinders for smooth operation in high-temperature environments. Special seals handle extreme temperatures.
Engine and Powertrain Assembly
Engine assembly lines use compact rodless cylinders for component insertion and testing operations. Space savings allow more operations in smaller areas.
Transmission assembly equipment relies on rodless cylinders for component positioning and testing. Precise positioning ensures proper assembly alignment.
Cylinder head machining uses rodless cylinders for workpiece positioning and clamping. High force capacity handles heavy castings securely.
Crankshaft grinding equipment uses rodless cylinders for workpiece feeding and positioning. Precise positioning ensures consistent surface finishes.
Final Assembly Operations
Final assembly lines use rodless cylinders for component installation and testing. The compact design allows more workstations in the same area.
Wheel installation equipment relies on rodless cylinders for wheel positioning and bolt tightening. Precise positioning ensures proper wheel alignment.
Door installation systems use rodless cylinders for door positioning and adjustment. Smooth operation prevents damage to painted surfaces.
Interior assembly equipment uses rodless cylinders for component installation and positioning. The clean operation prevents contamination of interior surfaces.
Quality Control and Testing
Automotive testing equipment uses rodless cylinders for sample positioning and testing operations. Precise positioning ensures accurate test results.
Leak testing systems rely on rodless cylinders for part positioning and sealing. Consistent operation ensures reliable test results.
Durability testing equipment uses rodless cylinders for load application and positioning. High force capacity handles heavy test loads.
Dimensional inspection systems use rodless cylinders for part positioning and measurement. Precise positioning enables accurate quality control.
Where Do You Find Rodless Cylinders in Food and Pharmaceutical Industries?
Food and pharmaceutical industries require clean, sanitary operation that rodless cylinders provide. Regulatory compliance drives adoption of contamination-free designs.
Food and pharmaceutical industries use rodless cylinders in packaging equipment, filling machines, conveyor systems, processing equipment, and inspection systems where sanitary design, clean operation, and regulatory compliance are essential requirements.
Food Processing Equipment
Food processing machinery uses sanitary rodless cylinders for product handling and processing operations. Stainless steel construction meets food safety requirements.
Meat processing equipment relies on rodless cylinders for product positioning and cutting operations. Washdown capability handles harsh cleaning requirements.
Bakery equipment uses rodless cylinders for dough handling and product positioning. Smooth operation prevents damage to delicate products.
Dairy processing systems use rodless cylinders for container handling and filling operations. Sanitary design prevents contamination of dairy products.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Pharmaceutical packaging uses rodless cylinders for blister pack formation and tablet handling. Clean operation prevents contamination of sterile products.
Tablet pressing equipment relies on rodless cylinders for die positioning and pressure application. Precise positioning ensures consistent tablet quality.
Capsule filling machines use rodless cylinders for capsule positioning and filling operations. Clean operation maintains product sterility.
Liquid filling systems use rodless cylinders for container positioning and filling operations. Precise positioning ensures accurate fill volumes.
Packaging and Labeling
Food packaging machines use rodless cylinders for package forming and sealing operations. Sanitary design prevents product contamination.
Labeling equipment relies on rodless cylinders for label application and product positioning. Precise positioning ensures proper label placement.
Coding systems use rodless cylinders for print head positioning and product handling. Clean operation prevents ink contamination.
Inspection equipment uses rodless cylinders for product positioning and rejection. Precise positioning enables accurate quality control.
Conveyor and Handling Systems
Food conveyor systems use washdown-rated rodless cylinders for product handling and positioning. Stainless steel construction handles harsh cleaning chemicals.
Sorting equipment relies on rodless cylinders for product diverting and positioning. High-speed operation increases sorting throughput.
Accumulation systems use rodless cylinders for product stopping and releasing. Gentle operation prevents damage to delicate food products.
Transfer systems use rodless cylinders for product movement between processes. Smooth operation maintains product quality.
| Industry Application | Sanitary Requirements | Material Standards | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Washdown Capability | Stainless Steel | Clean Operation, Durability |
| Pharmaceutical | Sterile Operation | FDA Compliant | Contamination Prevention |
| Packaging | Clean Design | Food Grade | Reliability, Speed |
| Conveying | Smooth Surfaces | Corrosion Resistant | Easy Cleaning, Longevity |
How Are Rodless Cylinders Applied in Specialized Industrial Equipment?
Specialized industrial applications often have unique requirements that rodless cylinders address effectively. Custom solutions provide competitive advantages in niche markets.
Specialized industrial equipment uses rodless cylinders in printing presses, textile machinery, glass handling systems, solar panel manufacturing, and semiconductor equipment where specific performance requirements demand customized solutions.
Printing and Converting Equipment
Printing presses use rodless cylinders for paper feeding and registration systems. Precise positioning ensures accurate printing registration across multiple colors.
Web handling equipment relies on rodless cylinders for tension control and web positioning. Consistent operation maintains product quality throughout the process.
Die cutting machines use rodless cylinders for material feeding and cutting operations. Precise positioning ensures accurate cutting patterns.
Laminating equipment uses rodless cylinders for material feeding and pressure application. Smooth operation prevents wrinkles and air bubbles.
Textile Manufacturing
Textile machinery uses rodless cylinders for fabric handling, cutting, and processing operations. Smooth operation prevents fabric damage during processing.
Weaving equipment relies on rodless cylinders for warp and weft positioning. Precise positioning ensures consistent fabric quality.
Knitting machines use rodless cylinders for yarn feeding and fabric handling. Gentle operation prevents yarn breakage.
Dyeing equipment uses rodless cylinders for fabric positioning and handling. Chemical-resistant construction handles harsh dyeing chemicals.
Glass and Ceramics Processing
Glass handling systems use rodless cylinders for sheet positioning and transport. Smooth operation prevents glass breakage during handling.
Ceramic processing equipment relies on rodless cylinders for product positioning and forming. Precise positioning ensures consistent product dimensions.
Glazing systems use rodless cylinders for product positioning and coating application. Smooth operation ensures even coating distribution.
Firing equipment uses rodless cylinders for product loading and unloading. High-temperature construction handles extreme operating conditions.
Solar Panel Manufacturing
Solar panel production uses rodless cylinders for cell positioning and assembly operations. Clean operation prevents contamination of sensitive surfaces.
Laminating equipment relies on rodless cylinders for panel positioning and pressure application. Precise positioning ensures proper layer alignment.
Testing systems use rodless cylinders for panel positioning and electrical testing. Accurate positioning enables reliable test results.
Packaging equipment uses rodless cylinders for panel handling and packaging operations. Gentle operation prevents damage to finished panels.
Semiconductor Equipment
Wafer handling systems use ultra-clean rodless cylinders for wafer positioning and transport. Contamination-free operation is critical for yield.
Lithography5 equipment relies on rodless cylinders for wafer positioning and exposure operations. Precise positioning ensures accurate pattern transfer.
Etching systems use rodless cylinders for wafer positioning and processing. Chemical-resistant construction handles aggressive chemicals.
Assembly equipment uses rodless cylinders for die positioning and bonding operations. Precise positioning ensures reliable electrical connections.
Conclusion
Rodless cylinders find applications across diverse industries where space efficiency, long strokes, and precise positioning are essential. Understanding specific application requirements helps select the optimal solution for each use case.
FAQs About Rodless Cylinder Applications
What industries use rodless cylinders most frequently?
Automotive manufacturing, packaging and food processing, pharmaceutical production, electronics assembly, and material handling industries use rodless cylinders most frequently due to space constraints and precision requirements.
Where are rodless cylinders used in automotive manufacturing?
Automotive applications include body-in-white assembly, welding fixtures, paint line conveyors, engine assembly, powertrain manufacturing, and quality testing equipment where space efficiency and precise positioning are critical.
How are rodless cylinders applied in packaging machinery?
Packaging applications include form-fill-seal machines, cartoning equipment, labeling systems, conveyor operations, and palletizing systems where long strokes, high speeds, and compact designs are essential.
What food and pharmaceutical applications use rodless cylinders?
Food and pharmaceutical industries use rodless cylinders in processing equipment, packaging machines, filling systems, conveyor operations, and inspection equipment where sanitary design and clean operation are required.
Which specialized industrial equipment uses rodless cylinders?
Specialized applications include printing presses, textile machinery, glass handling systems, solar panel manufacturing, and semiconductor equipment where specific performance requirements demand customized solutions.
What are the main benefits of using rodless cylinders in industrial applications?
Main benefits include 50% space savings compared to traditional cylinders, long stroke capabilities up to 10 meters, improved safety by eliminating exposed rods, and better performance in contaminated environments.
How do you determine if rodless cylinders are right for your application?
Consider rodless cylinders when space is limited, stroke lengths exceed 500mm, side loads are present, safety concerns exist with exposed rods, or when traditional cylinders would interfere with surrounding equipment.
-
Learn the definition of “Body-in-White” (BIW) and its significance in the automotive assembly process. ↩
-
See a technical animation and explanation of the horizontal form-fill-seal (HFFS) packaging process. ↩
-
Explore the working principles of Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) and their role in precision metrology. ↩
-
View a guide on the hemming process for joining sheet metal panels in automotive and industrial applications. ↩
-
Understand the fundamental steps of the photolithography process used in semiconductor and microchip fabrication. ↩


