Your pneumatic system was working perfectly during installation, but three months later you’re dealing with persistent air leaks at every connection. The maintenance team keeps tightening the fittings, but the leaks return within days. The problem isn’t loose connections—it’s thread type mismatch. Someone mixed NPT and BSP fittings, creating connections that appear to work but can never seal properly. Understanding thread types and sealing methods isn’t just technical knowledge—it’s the foundation of leak-free pneumatic systems. 🔧
Thread type selection and proper sealing methods are critical for pneumatic system reliability, with NPT threads using taper interference for sealing, BSP threads requiring gaskets or sealants, and G threads designed for O-ring sealing, each demanding specific installation techniques and compatible components for leak-free operation.
Just yesterday, I helped Jennifer, a maintenance supervisor at an automotive plant in Ohio, solve chronic air leaks that were costing $15,000 annually in wasted compressed air—the root cause was mixing incompatible thread types throughout their pneumatic system.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Fundamental Differences Between Thread Types?
- How Do Different Sealing Methods Work with Each Thread Type?
- What Are the Application-Specific Advantages and Limitations?
- How Do You Select and Implement the Right Thread and Sealing System?
What Are the Fundamental Differences Between Thread Types?
Understanding the geometric and functional differences between NPT, BSP, and G threads is essential for proper selection and installation of pneumatic valve connections.
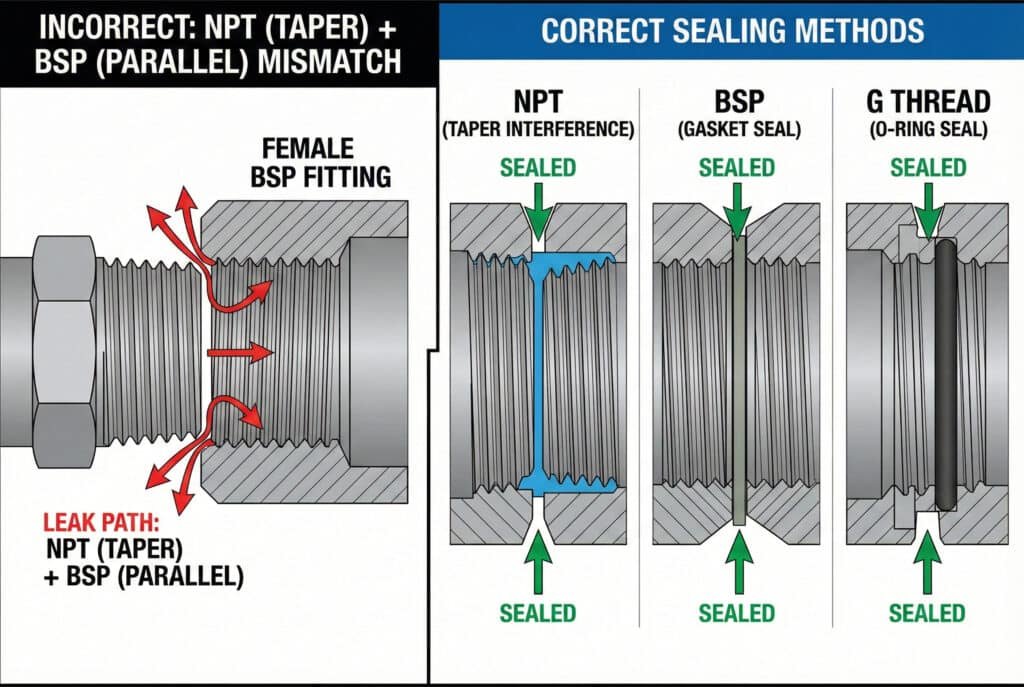
Thread types differ fundamentally in their geometry, sealing mechanisms, and regional standards, with NPT using 60° tapered threads for interference sealing, BSP employing 55° threads with various sealing methods, and G threads utilizing parallel geometry designed for O-ring sealing systems.

NPT (National Pipe Thread) Characteristics
NPT threads feature a 60-degree thread angle with 1:16 taper1 (3/4 inch per foot), creating interference fit sealing through thread deformation. The taper design provides both mechanical connection and primary sealing.
BSP (British Standard Pipe) Thread Variations
BSP threads use a 55-degree thread angle and come in two main types: BSPT (tapered) similar to NPT function, and BSPP (parallel)2 requiring separate sealing methods.
G Thread (ISO 228) Specifications
G threads are parallel (straight) threads with 55-degree angles, designed specifically for O-ring or gasket sealing rather than thread interference sealing. The official specification for these threads is ISO 2283.
Thread Pitch and Sizing Standards
Different thread standards use varying pitch specifications and sizing conventions that affect compatibility and performance.
| Thread Type | Angle | Taper | Sealing Method | Common Sizes | Regional Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPT | 60° | 1:16 taper | Thread interference | 1/8″ to 4″ | North America |
| BSPT | 55° | 1:16 taper | Thread interference | 1/8″ to 6″ | UK, Commonwealth |
| BSPP/G | 55° | Parallel | O-ring/gasket | 1/8″ to 6″ | Europe, Asia |
| Metric M | 60° | Parallel | O-ring/gasket | M5 to M64 | Global metric |
Jennifer’s automotive plant had mixed NPT and BSP fittings throughout their system. The 60° vs 55° thread angle difference meant connections appeared tight but couldn’t seal properly, causing persistent leaks. 💨
Thread Engagement and Strength
Different thread types have varying engagement characteristics that affect joint strength, sealing effectiveness, and installation torque requirements.
Compatibility and Interchangeability Issues
Thread type mixing creates serious compatibility problems that can appear to work initially but fail over time due to improper sealing and stress concentration.
How Do Different Sealing Methods Work with Each Thread Type?
Each thread type employs specific sealing mechanisms that must be properly understood and implemented to achieve reliable, leak-free connections.
Sealing methods vary significantly between thread types: NPT relies on thread deformation and sealant for primary sealing, BSP uses thread sealant or gaskets depending on taper or parallel design, while G threads require O-rings or face seals for effective sealing, each demanding specific installation procedures and materials.
NPT Thread Sealing Mechanisms
NPT threads create primary sealing through metal-to-metal interference as the tapered male thread wedges into the female thread, with thread sealant filling micro-gaps for complete sealing.
Thread Sealant Applications
Thread sealants including PTFE tape, liquid sealants, and anaerobic compounds4 fill thread gaps and prevent leakage while allowing proper thread engagement.
O-Ring Sealing Systems
O-ring sealing uses elastomeric rings compressed in designed grooves to create positive sealing independent of thread engagement, commonly used with G threads.
Face Seal and Gasket Methods
Face sealing compresses gaskets or O-rings between mating surfaces, providing sealing independent of thread type while threads provide only mechanical retention.
| Sealing Method | Thread Compatibility | Pressure Rating | Temperature Range | Installation Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thread interference | NPT, BSPT | High | -65°F to +400°F | Proper engagement, sealant |
| PTFE tape | NPT, BSPT, BSPP | Medium-high | -100°F to +500°F | Correct wrapping, tension |
| Liquid sealant | All types | High | Variable | Clean threads, cure time |
| O-ring seal | G, BSPP, Metric | Very high | Material dependent | Proper groove design |
Sealant Selection Criteria
Sealant selection depends on Media compatibility5, temperature range, pressure requirements, and disassembly needs, with different formulations optimized for specific applications.
Installation Torque Requirements
Proper installation torque varies by thread type and sealing method, with over-tightening potentially damaging threads or seals while under-tightening causes leaks.
Our Bepto engineering team has developed comprehensive sealing protocols that specify exact procedures for each thread type and application, eliminating installation errors and ensuring reliable sealing. 🛠️
Seal Integrity Testing
Proper testing procedures verify seal integrity after installation, including pressure testing, leak detection, and long-term monitoring to ensure continued performance.
What Are the Application-Specific Advantages and Limitations?
Different thread types and sealing methods offer distinct advantages and limitations that make them suitable for specific applications while potentially problematic in others.
Application-specific selection requires matching thread type advantages to system requirements: NPT excels in high-pressure applications with simple installation, BSP provides flexibility with multiple sealing options, and G threads offer superior sealing reliability for precision applications, each with specific limitations and optimal use cases.
NPT Thread Applications
NPT threads excel in high-pressure pneumatic systems, industrial applications, and situations requiring simple installation without additional sealing components.
BSP Thread Versatility
BSP threads offer flexibility with both tapered and parallel options, making them suitable for diverse applications from low-pressure pneumatics to high-pressure hydraulics.
G Thread Precision Applications
G threads provide superior sealing reliability for precision applications, clean environments, and systems requiring frequent disassembly and reassembly.
Industry-Specific Preferences
Different industries have established preferences based on historical usage, regulatory requirements, and performance characteristics.
| Application Type | Preferred Thread | Primary Advantages | Typical Limitations | Alternative Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial pneumatics | NPT | Simple installation, high pressure | Regional compatibility | BSP for international |
| Mobile hydraulics | BSP | Flexibility, availability | Complexity options | NPT for North America |
| Precision instruments | G | Reliable sealing, repeatability | Requires O-rings | BSP for simplicity |
| Process industries | Variable | Application-specific | Material compatibility | Specialized threads |
Pressure and Temperature Considerations
Different thread types handle pressure and temperature extremes differently, affecting their suitability for specific operating conditions.
Maintenance and Serviceability
Thread type selection impacts maintenance procedures, parts availability, and service technician training requirements.
I recently worked with Carlos, who manages a food processing facility in Mexico, where mixing NPT and metric threads created maintenance nightmares. Standardizing on G threads with O-ring sealing improved reliability while simplifying inventory. 🏭
Regulatory and Standards Compliance
Certain applications require specific thread types for regulatory compliance, safety standards, or industry specifications.
How Do You Select and Implement the Right Thread and Sealing System?
Systematic selection and implementation of thread types and sealing methods requires comprehensive analysis of application requirements, system constraints, and long-term considerations.
Optimal thread and sealing system selection follows a systematic process: analyze application requirements including pressure, temperature, and media compatibility, evaluate system constraints and regional standards, select appropriate thread type and sealing method, and implement proper installation procedures with quality verification.
Application Requirements Analysis
Document all system requirements including operating pressure, temperature range, media compatibility, vibration levels, and environmental conditions that affect thread and seal performance.
System Standardization Strategy
Develop standardization strategies that minimize thread type variety while meeting all application requirements, reducing inventory complexity and training needs.
Regional and Regulatory Considerations
Consider regional thread preferences, supplier availability, and regulatory requirements that may mandate specific thread types or sealing methods.
Economic Analysis Framework
Evaluate total cost including initial hardware costs, installation labor, maintenance requirements, and long-term reliability to optimize economic value.
| Selection Criteria | Weight Factor | NPT Score | BSP Score | G Thread Score | Decision Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Installation simplicity | Medium | 9/10 | 7/10 | 6/10 | Labor costs, training |
| Sealing reliability | High | 7/10 | 8/10 | 9/10 | System performance |
| Pressure capability | High | 9/10 | 8/10 | 9/10 | Safety, performance |
| Parts availability | Medium | Variable | Variable | Variable | Regional considerations |
| Maintenance ease | Medium | 8/10 | 7/10 | 8/10 | Long-term costs |
Installation Procedure Development
Develop detailed installation procedures specific to each thread type and sealing method, including torque specifications, sealant application, and quality verification steps.
Quality Control and Testing
Implement quality control procedures including thread inspection, seal verification, and pressure testing to ensure proper installation and performance.
Jennifer’s automotive plant implemented a comprehensive thread standardization program that reduced leak-related downtime by 85% while simplifying maintenance procedures and reducing inventory costs. 📊
Training and Documentation
Provide comprehensive training for installation and maintenance personnel on proper procedures for each thread type and sealing method used in the system.
Performance Monitoring and Optimization
Establish monitoring systems to track connection performance and identify opportunities for further optimization or standardization.
Proper thread type selection and sealing method implementation are fundamental to pneumatic system reliability, requiring systematic analysis and careful attention to installation details.
FAQs About Valve Port Thread Types and Sealing Methods
Q: Can I mix different thread types in the same pneumatic system?
While physically possible in some cases, mixing thread types creates compatibility issues, increases leak potential, and complicates maintenance. Standardization on one thread type is strongly recommended.
Q: How do I identify what thread type I have on existing equipment?
Use thread pitch gauges and angle measurements to identify thread type. NPT has 60° angles, BSP/G have 55° angles, and taper can be measured with proper gauges.
Q: What’s the best sealant for NPT threads in pneumatic applications?
PTFE tape is most common for pneumatic NPT connections, though liquid anaerobic sealants work well for permanent installations. Avoid pipe dope in clean air systems.
Q: Why do my NPT connections keep leaking even when tight?
Common causes include damaged threads, incorrect sealant application, over-tightening causing thread damage, or mixing incompatible thread types.
Q: Are there adapters to convert between different thread types?
Yes, thread adapters exist but add potential leak points and system complexity. Direct standardization is preferred when possible.
-
Discover the exact geometric specification that defines the interference fit and sealing mechanism of NPT threads. ↩
-
Clarify the distinction between BSPP and the G thread standard, focusing on how parallel threads achieve reliable sealing. ↩
-
Consult the official international standard that specifies the dimensions and characteristics of G series (parallel) pipe threads. ↩
-
Learn about the chemical sealants that cure in the absence of air, providing a permanent and pressure-resistant thread seal. ↩
-
Understand the chemical interaction between system materials (seals, threads) and the compressed air or gas media used. ↩



