After 20 years in pneumatic systems1, I’ve seen the same costly mistakes repeated thousands of times—engineers spending hours chasing complex solutions when the root cause2 is often a simple, overlooked fault. These troubleshooting delays cost manufacturers an average of $50,000 per incident in lost production, emergency repairs, and rushed replacement parts. 😰
Effective pneumatic cylinder troubleshooting requires systematic diagnosis of air supply issues, seal failures, contamination problems, and mechanical wear patterns using pressure testing, visual inspection, and performance measurement techniques to identify root causes quickly and prevent recurring failures.
Last month, I helped Jennifer, a maintenance engineer at a packaging facility in Texas, who was facing daily cylinder failures that had stumped her team for weeks—until we discovered a simple air dryer malfunction was destroying seals throughout her entire pneumatic system.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Most Common Pneumatic Cylinder Failure Modes?
- How Do You Diagnose Air Supply and Pressure-Related Issues?
- Which Seal and Internal Component Failures Cause Performance Problems?
- What Systematic Approach Ensures Accurate Fault Diagnosis?
What Are the Most Common Pneumatic Cylinder Failure Modes?
Understanding failure patterns helps technicians focus troubleshooting efforts on the most probable causes, reducing diagnostic time and preventing misdiagnosis.
Common pneumatic cylinder failures include internal air leakage from worn seals causing slow operation, external leakage reducing system pressure, contamination damage creating erratic movement, mechanical binding from misalignment, and valve malfunctions preventing proper directional control.
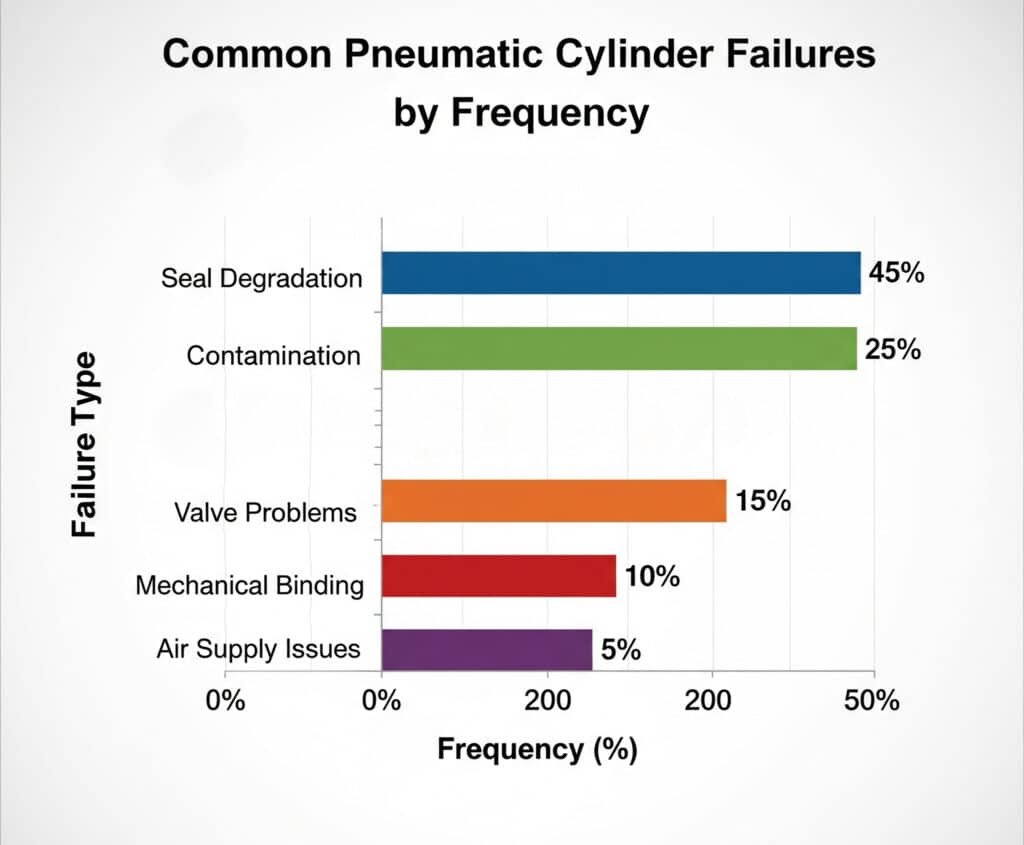
Primary Failure Categories
Through analyzing thousands of field failures, I’ve categorized the most frequent issues:
| Failure Type | Frequency | Typical Symptoms | Average Repair Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seal Degradation | 45% | Slow operation, air leakage | $150-400 |
| Contamination | 25% | Erratic movement, sticking | $200-600 |
| Valve Problems | 15% | No movement, partial stroke | $100-300 |
| Mechanical Binding | 10% | Jerky motion, high pressure | $300-800 |
| Air Supply Issues | 5% | Inconsistent performance | $50-200 |
Seal-Related Failures
Seal problems manifest in predictable patterns:
- Internal leakage causes gradual speed reduction and weak force output
- External leakage creates visible air loss and pressure drops
- Seal extrusion from pressure spikes damages housing grooves
- Chemical attack from contaminated air supply accelerates degradation
Contamination Impact
Industrial environments assault pneumatic systems continuously:
- Moisture ingress causes internal corrosion and seal swelling
- Particulate contamination creates abrasive wear on seals and cylinders
- Oil contamination attacks elastomer seals and affects lubrication
- Chemical vapors degrade seal materials and metal surfaces
Bepto Reliability Advantage
Our Bepto cylinders incorporate design features that prevent common failures:
| Failure Mode | Standard Design | Bepto Protection | Reliability Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seal Wear | Basic seals | Premium compounds | 300% longer life |
| Contamination | Standard filtration | Integrated protection | 400% better resistance |
| Binding | Basic guides | Precision bearings | 200% smoother operation |
| Corrosion | Standard coatings | Advanced treatments | 500% better protection |
How Do You Diagnose Air Supply and Pressure-Related Issues?
Air supply problems often masquerade as cylinder failures, leading to unnecessary component replacement when system-level issues are the actual cause.
Accurate air supply diagnosis requires measuring static and dynamic pressures at multiple system points, checking air quality for moisture and contamination, verifying flow rates under load conditions, and testing pressure regulation stability during operation cycles.
Pressure System Analysis
Systematic Pressure Testing
Effective diagnosis follows a structured approach:
- Static pressure measurement at compressor output
- Dynamic pressure testing during cylinder operation
- Pressure drop analysis across system components
- Flow rate verification under maximum load conditions
Common Pressure-Related Symptoms
| Symptom | Probable Cause | Diagnostic Test | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow extension | Low supply pressure | Gauge at cylinder | Increase pressure/check supply |
| Weak force output | Pressure drop under load | Dynamic pressure test | Upgrade air lines/valves |
| Inconsistent speed | Pressure regulation issues | Pressure stability test | Replace regulator |
| No movement | Complete pressure loss | System pressure check | Find major leak/blockage |
Air Quality Assessment
Poor air quality destroys pneumatic systems from within:
- Moisture content should be below -40°C pressure dew point3
- Particulate filtration must remove particles >5 microns
- Oil content should be <1 ppm for seal compatibility
- Chemical contamination requires specialized filtration
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
Professional troubleshooting requires proper instrumentation:
- Digital pressure gauges for accurate readings
- Flow meters for capacity verification
- Air quality analyzers for contamination detection
- Leak detection equipment for system integrity
Robert, a plant engineer from a pharmaceutical facility in Massachusetts, discovered that his “cylinder failures” were actually caused by undersized air lines that couldn’t maintain pressure during high-demand periods. Upgrading his distribution system eliminated 90% of his performance complaints. 🔧
Which Seal and Internal Component Failures Cause Performance Problems?
Internal component degradation creates specific performance signatures that experienced technicians can identify through systematic observation and testing.
Critical internal failures include piston seal wear causing internal leakage and reduced force, rod seal degradation creating external leakage, bearing wear producing alignment issues, and guide system damage causing binding and erratic motion patterns.
Internal Component Diagnosis
Seal Failure Patterns
Different seal failures create distinct symptoms:
| Seal Location | Failure Mode | Performance Impact | Diagnostic Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piston Seal | Internal leakage | Slow operation, weak force | Pressure decay test4 |
| Rod Seal | External leakage | Air loss, contamination entry | Visual inspection |
| End Cap Seals | Port leakage | Pressure loss at connections | Soap bubble test |
| Guide Seals | Contamination ingress | Erratic movement | Performance monitoring |
Bearing and Guide System Issues
Mechanical wear creates progressive performance degradation:
- Bearing clearance increase causes alignment problems and vibration
- Guide rail wear creates binding and inconsistent motion
- Shaft scoring from contamination damages seals and guides
- Housing bore wear affects seal performance and pressure retention
Performance Testing Methods
Systematic testing reveals internal component condition:
- Pressure decay testing quantifies internal leakage rates
- Force output measurement indicates seal and pressure integrity
- Speed consistency testing reveals binding and wear issues
- Positioning accuracy shows guide system condition
Bepto Component Quality
Our internal components are engineered for extended service life:
- Premium seal materials resist chemical attack and wear
- Precision-machined surfaces ensure optimal seal contact
- Advanced bearing systems provide smooth, long-lasting operation
- Integrated contamination protection prevents premature wear
Michael, a maintenance supervisor at an automotive parts facility in Ohio, extended his cylinder service intervals from 6 months to 3 years by switching to Bepto cylinders with superior internal components, saving his facility $25,000 annually in maintenance costs. 💪
What Systematic Approach Ensures Accurate Fault Diagnosis?
Effective troubleshooting follows a logical sequence that prevents misdiagnosis and ensures root cause identification rather than symptom treatment.
Systematic diagnosis requires documenting baseline performance parameters, following structured testing sequences from system level to component level, recording all measurements and observations, and verifying repairs through performance testing before returning equipment to service.
Diagnostic Methodology
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Process
Professional diagnosis follows this proven sequence:
- Symptom documentation with specific performance measurements
- System-level testing to isolate cylinder vs. system issues
- Component-level diagnosis focusing on most probable causes
- Root cause verification through targeted testing
- Repair validation confirming problem resolution
Diagnostic Decision Tree
| Initial Symptom | First Check | If Normal | If Abnormal |
|---|---|---|---|
| No movement | System pressure | Check valve operation | Restore pressure/find leak |
| Slow operation | Supply pressure | Test internal leakage | Increase pressure |
| Erratic motion | Air quality | Check mechanical binding | Clean/filter air supply |
| Weak force | Pressure under load | Test seal condition | Upgrade air supply |
Documentation and Tracking
Effective troubleshooting requires comprehensive records:
- Performance baselines for comparison during diagnosis
- Failure history to identify recurring patterns
- Environmental conditions affecting component life
- Maintenance records showing service intervals and parts
Bepto Diagnostic Support
We provide comprehensive troubleshooting resources:
- Technical documentation with detailed diagnostic procedures
- Performance specifications for baseline comparisons
- Failure analysis services for complex problems
- Application engineering support for system optimization
Validation and Prevention
Successful troubleshooting includes prevention strategies:
- Performance monitoring to detect degradation trends
- Preventive maintenance5 based on actual condition
- System upgrades to eliminate recurring problems
- Training programs for maintenance personnel
Conclusion
Systematic pneumatic cylinder troubleshooting using structured diagnostic procedures, proper instrumentation, and comprehensive documentation ensures accurate fault identification and prevents costly misdiagnosis in industrial applications.
FAQs About Troubleshooting Pneumatic Cylinder Faults
Q: What’s the most common mistake in pneumatic cylinder troubleshooting?
A: The most common mistake is replacing cylinders when the actual problem is system-level, such as inadequate air supply or contamination. Always test system conditions before assuming component failure to avoid unnecessary replacement costs.
Q: How do you distinguish between internal and external seal failures?
A: Internal seal failures cause slow operation and reduced force while maintaining system pressure, whereas external seal failures create visible air leakage and pressure loss. Use pressure decay testing to quantify internal leakage rates accurately.
Q: What diagnostic tools are essential for effective pneumatic troubleshooting?
A: Essential tools include digital pressure gauges for accurate readings, flow meters for capacity testing, air quality analyzers for contamination detection, and leak detection equipment. Invest in quality instruments for reliable diagnosis.
Q: How do you prevent recurring pneumatic cylinder failures?
A: Prevention requires addressing root causes rather than symptoms through proper air treatment, contamination control, appropriate sizing, and condition-based maintenance. Document failure patterns to identify and eliminate systemic issues.
Q: When should you repair versus replace a faulty pneumatic cylinder?
A: Replace cylinders when repair costs exceed 60% of replacement cost, when multiple components are worn, or when failures occur frequently. Consider upgrading to higher-quality components like Bepto cylinders to reduce long-term maintenance costs.
-
Learn the basic principles of pneumatic systems, which use compressed air to transmit and control energy. ↩
-
Explore common Root Cause Analysis (RCA) methods like the 5 Whys and Fishbone Diagrams used to solve problems. ↩
-
Understand this critical metric for compressed air quality and how it relates to moisture content. ↩
-
Discover the procedure for pressure decay testing, a quantitative method for detecting and measuring leaks in sealed components. ↩
-
Learn about this proactive maintenance strategy that involves regular, scheduled inspections and service to prevent equipment failures. ↩