Engineers often underestimate the total cost implications when choosing between pneumatic cylinders and electric actuators, leading to budget overruns and unexpected maintenance expenses throughout the system lifecycle.
Pneumatic cylinders typically cost 50-75% less than electric actuators initially, with significantly lower installation, maintenance, and training costs, though electric actuators may offer energy savings in specific continuous-duty applications, making total cost of ownership1 analysis crucial for optimal selection.
Yesterday, Jennifer from a Canadian manufacturing facility discovered her “cost-effective” electric actuator project was running 180% over budget due to unexpected programming, installation complexity, and specialized maintenance requirements that pneumatic cylinders would have avoided entirely.
Table of Contents
- How Do Initial Purchase Costs Compare Between Cylinders and Electric Actuators?
- What Are the Hidden Installation and Setup Cost Differences?
- How Do Long-Term Operating and Maintenance Costs Compare?
- Which Technology Offers Better Total Cost of Ownership Over Five Years?
How Do Initial Purchase Costs Compare Between Cylinders and Electric Actuators?
Understanding upfront investment differences helps engineers make informed budget decisions and avoid costly specification errors during project planning phases.
Pneumatic cylinders cost 50-75% less than equivalent electric actuators initially, with standard cylinders ranging from $50-$500 while comparable electric actuators cost $200-$2000, plus additional controller and programming expenses that can double the total electric system investment.

Direct Component Price Comparison
Pneumatic Cylinder Pricing Structure
Cylinder costs remain straightforward and predictable:
- Standard cylinders: $50-$500 depending on bore size and stroke
- Rodless air cylinders2: $150-$800 for long-stroke applications
- Mini cylinders: $30-$200 for compact precision work
- Heavy-duty units: $200-$1200 for industrial applications
Electric Actuator Pricing Reality
Electric systems demand significantly higher investment:
- Basic electric actuators: $200-$1500 for equivalent force/stroke
- Servo actuators: $800-$3000 for precision applications
- Linear motors: $1500-$5000 for high-performance needs
- Complete systems: Often 3-5x cylinder cost including controllers
Bepto Cost Advantage Analysis
Competitive Pricing Comparison Matrix
| Force Range | Bepto Cylinder | OEM Cylinder | Electric Actuator | Bepto Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100-500 lbf | $85-$280 | $150-$450 | $400-$1200 | 65-80% |
| 500-1500 lbf | $180-$520 | $300-$850 | $800-$2500 | 70-85% |
| 1500-3000 lbf | $350-$750 | $600-$1300 | $1500-$4000 | 75-85% |
| 3000+ lbf | $600-$1200 | $1000-$2000 | $2500-$6000 | 70-80% |
Supporting Component Costs
Pneumatic System Requirements
Cylinder systems need basic supporting components:
- Solenoid valves3: $25-$150 for directional control
- Pressure regulators: $30-$100 for force control
- Flow controls: $15-$50 for speed adjustment
- Pneumatic fittings: $5-$25 per connection point
Electric System Dependencies
Electric actuators require expensive supporting equipment:
- Motion controllers: $500-$3000 for basic positioning
- Servo drives: $400-$2500 for motor control
- Feedback devices: $100-$800 for position sensing
- Programming software: $200-$1500 licensing costs
Volume Pricing Advantages
Quantity Discount Structure
Bepto offers aggressive volume pricing:
| Order Quantity | Standard Discount | Rodless Cylinder Discount | Additional Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-5 units | List price | List price | Standard warranty |
| 6-25 units | 10% discount | 12% discount | Extended warranty |
| 26-100 units | 18% discount | 20% discount | Custom modifications |
| 100+ units | 25% discount | 28% discount | Dedicated support |
Project-Based Pricing
Large projects receive additional considerations:
- System packages: Bundled pricing for complete solutions
- Engineering support: Included technical consultation
- Custom modifications: No additional tooling charges
- Delivery scheduling: Coordinated shipments to reduce costs
Regional Cost Variations
Geographic Pricing Factors
Costs vary by market region:
- North America: Premium pricing for electric systems
- Europe: High labor costs favor simple pneumatic installation
- Developing markets: Pneumatic systems offer significant advantages
- Remote locations: Pneumatic simplicity reduces service costs
Currency and Trade Considerations
International factors affect pricing:
- Exchange rates: Pneumatic components less affected by currency fluctuations
- Import duties: Electric systems often face higher tariff rates
- Local content: Pneumatic systems easier to source locally
- Service availability: Pneumatic support more widely available
What Are the Hidden Installation and Setup Cost Differences?
Installation complexity and setup requirements create significant cost differences that often exceed initial component price variations between pneumatic and electric systems.
Pneumatic cylinder installation typically requires 60-80% less time and specialized labor compared to electric actuators, with simple air connections versus complex electrical wiring, programming, and commissioning that can add $1000-$5000 per actuator in hidden costs.
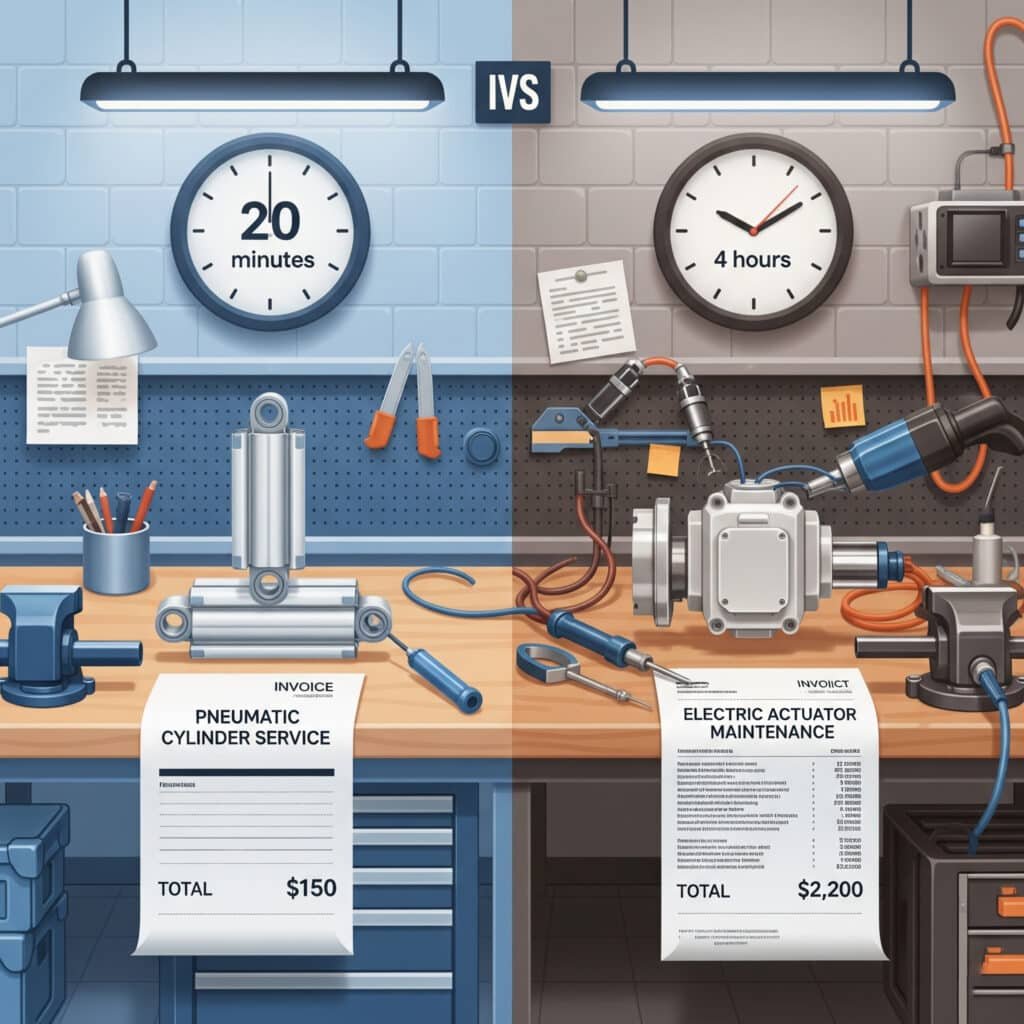
Installation Labor Requirements
Pneumatic Installation Simplicity
Cylinder installation remains straightforward:
- Connection time: 15-30 minutes for basic cylinder installation
- Skill level: Standard maintenance technicians can install
- Tools required: Basic hand tools and pneumatic fittings
- Testing procedure: Simple pressure test and cycle verification
Electric Installation Complexity
Electric actuators demand specialized installation:
- Installation time: 2-8 hours including wiring and programming
- Skill requirements: Certified electricians and programmers needed
- Specialized tools: Programming devices and diagnostic equipment
- Commissioning: Complex setup and parameter tuning required
Infrastructure Requirements
Pneumatic Infrastructure Costs
Most facilities have existing compressed air systems:
| Infrastructure Element | Typical Cost | Installation Time | Maintenance Need |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air supply connection | $50-$200 | 30 minutes | Minimal |
| Pressure regulation | $75-$150 | 45 minutes | Annual check |
| Flow control | $25-$100 | 15 minutes | Rare adjustment |
| Safety shutoff | $100-$300 | 1 hour | Annual test |
Electric Infrastructure Investment
Electric systems often require new infrastructure:
- Power supply: $200-$1000 for dedicated circuits
- Control panels: $500-$3000 for motion control systems
- Communication networks: $300-$1500 for system integration
- Safety systems: $400-$2000 for emergency stops and interlocks
Programming and Commissioning Costs
Pneumatic Commissioning
Cylinder systems require minimal setup:
- Parameter setting: Basic pressure and flow adjustments
- Safety testing: Simple cycle verification and emergency stops
- Documentation: Standard installation and maintenance procedures
- Training: 1-2 hours for operators and maintenance staff
Electric System Programming
Electric actuators demand extensive commissioning:
- Motion programming: 4-20 hours for complex motion profiles
- Safety integration: Extensive testing and validation procedures
- System integration: Network communication and data exchange setup
- Operator training: 8-40 hours for programming and troubleshooting
Project Timeline Impact
Pneumatic Project Scheduling
Cylinder installations fit standard project timelines:
- Design phase: Standard pneumatic schematics and specifications
- Procurement: 5-10 day delivery for most Bepto components
- Installation: Same-day installation and commissioning possible
- Startup: Immediate operation after basic testing
Electric Project Extensions
Electric systems often extend project schedules:
- Design complexity: Detailed electrical and programming specifications
- Lead times: 4-12 weeks for electric actuators and controllers
- Installation delays: Specialized contractor scheduling requirements
- Debugging time: Troubleshooting and optimization periods
Training and Support Costs
Pneumatic Training Requirements
Minimal training investment needed:
- Operator training: Basic operation and safety procedures
- Maintenance training: Standard pneumatic component service
- Troubleshooting: Visual and audible diagnostic techniques
- Documentation: Simple maintenance and parts manuals
Electric Training Investment
Electric systems require extensive training:
- Programming training: $2000-$5000 per technician
- Diagnostic training: Specialized equipment and procedures
- Safety certification: Additional electrical safety requirements
- Ongoing education: Regular updates for software and technology changes
Michael, a project manager at a Michigan automotive supplier, initially budgeted $15,000 for electric actuators on his new assembly line. After accounting for programming, installation complexity, and training requirements, his total project cost reached $38,000. Switching to Bepto rodless cylinders reduced his total project cost to $12,000 while meeting all performance requirements.
How Do Long-Term Operating and Maintenance Costs Compare?
Ongoing operational expenses and maintenance requirements create substantial cost differences between pneumatic and electric actuator systems over their service life.
Pneumatic cylinders typically require 60-80% lower annual maintenance costs compared to electric actuators, with simple seal replacement and basic air system maintenance versus complex electronic diagnostics, motor service, and specialized programming support that electric systems demand.

Annual Maintenance Cost Analysis
Pneumatic Maintenance Requirements
Cylinder maintenance remains simple and cost-effective:
- Routine service: $50-$150 per year for basic maintenance
- Seal replacement: $25-$100 every 2-5 years depending on duty
- Air system maintenance: $100-$300 annually for filtration and lubrication
- Emergency repairs: $75-$200 for typical field repairs
Electric Actuator Maintenance Expenses
Electric systems demand specialized and expensive service:
- Annual service: $200-$800 for preventive maintenance programs
- Motor service: $300-$1500 for brush replacement and bearing service
- Electronic repairs: $500-$3000 for controller and feedback device issues
- Software updates: $200-$1000 annually for programming and calibration
Energy Consumption Comparison
Pneumatic Energy Analysis
Air system energy costs depend on duty cycle:
| Duty Cycle | Cylinder Size | Annual Energy Cost | Efficiency Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intermittent | 2″ bore | $150-$400 | Good for short cycles |
| Moderate | 4″ bore | $300-$800 | Reasonable for medium duty |
| Heavy | 6″ bore | $600-$1500 | Acceptable for high force |
| Continuous | Any size | Variable | Less efficient than electric |
Electric Energy Consumption
Electric actuators show different energy profiles:
- Standby power: Continuous controller power consumption
- Motion energy: Efficient during actual movement
- Regenerative capability4: Some energy recovery during deceleration
- Load dependency: Energy consumption varies with application load
Parts and Service Availability
Pneumatic Parts Accessibility
Cylinder components remain widely available:
- Standard parts: Common seals and components from multiple suppliers
- Bepto advantage: 40-60% savings on replacement parts
- Local service: Most technicians can service pneumatic components
- Emergency availability: Standard parts available from local distributors
Electric Parts Challenges
Electric actuator service presents complications:
- Proprietary components: Manufacturer-specific parts and programming
- Obsolescence risk: Electronic components become unavailable
- Specialized service: Factory-trained technicians often required
- Emergency costs: Premium pricing for urgent electric repairs
Downtime Cost Impact
Pneumatic Reliability Advantages
Cylinder systems minimize production interruptions:
- Simple diagnostics: Visual and audible problem identification
- Quick repairs: Most issues resolved in minutes to hours
- Backup options: Manual override capabilities available
- Preventive maintenance: Scheduled during planned downtime
Electric System Downtime Risks
Electric actuators can cause extended outages:
- Complex diagnostics: Specialized equipment and expertise required
- Repair delays: Parts ordering and factory service scheduling
- Programming issues: Software problems requiring specialist support
- System integration: Network and communication troubleshooting
Total Maintenance Cost Projection
Five-Year Maintenance Comparison
| Cost Category | Pneumatic Cylinder | Electric Actuator | Cost Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Routine maintenance | $250-$750 | $1000-$4000 | 75-85% savings |
| Parts replacement | $100-$500 | $800-$3000 | 80-85% savings |
| Emergency repairs | $150-$600 | $1000-$5000 | 80-90% savings |
| Training costs | $200-$500 | $2000-$8000 | 85-95% savings |
| Total 5-year | $700-$2350 | $4800-$20000 | 80-90% savings |
Service Contract Considerations
Pneumatic Service Options
Cylinder service remains flexible and affordable:
- In-house capability: Most maintenance performed by plant staff
- Local service: Regional pneumatic specialists available
- Bepto support: Direct technical assistance and parts supply
- Flexible contracts: Pay-as-needed or annual agreements
Electric Service Requirements
Electric systems often require expensive service contracts:
- Mandatory contracts: Some manufacturers require service agreements
- Specialized support: Factory-trained technician requirements
- Software licensing: Ongoing programming and diagnostic tool costs
- Escalating costs: Service prices increase with system complexity
Lisa, a maintenance manager at a Texas packaging facility, tracked her actuator costs over three years. Her pneumatic cylinders averaged $180 annually in maintenance costs, while comparable electric actuators required $1,200 per year including service contracts, parts, and specialized labor. The pneumatic systems also achieved 99.2% uptime versus 94.8% for the electric units.
Which Technology Offers Better Total Cost of Ownership Over Five Years?
Comprehensive five-year cost analysis reveals significant financial advantages for pneumatic cylinders in most industrial applications when considering all cost factors.
Pneumatic cylinders typically provide 60-80% lower total cost of ownership over five years compared to electric actuators, with savings from lower initial costs, simpler installation, reduced maintenance expenses, and minimal training requirements outweighing potential energy cost differences.
Comprehensive Cost Analysis Model
Five-Year Pneumatic System Costs
Complete pneumatic system investment breakdown:
- Initial purchase: $200-$800 for cylinder and basic controls
- Installation costs: $100-$300 for simple pneumatic connections
- Annual maintenance: $50-$150 per year for routine service
- Energy costs: $200-$800 annually depending on duty cycle
- Training investment: $200-$500 one-time cost
Five-Year Electric System Costs
Complete electric actuator system expenses:
- Initial purchase: $800-$3000 for actuator and controller
- Installation costs: $500-$2000 for complex electrical setup
- Annual maintenance: $200-$800 per year for specialized service
- Energy costs: $150-$600 annually for efficient operation
- Training investment: $2000-$5000 ongoing education requirements
Bepto Total Cost Advantage
Complete System Comparison Analysis
| Cost Component | 5-Year Pneumatic | 5-Year Electric | Bepto Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment cost | $800-$2000 | $3000-$8000 | 70-80% savings |
| Installation | $300-$800 | $1500-$5000 | 75-85% savings |
| Maintenance | $500-$1500 | $2500-$8000 | 70-85% savings |
| Energy | $1500-$4000 | $1000-$3000 | Variable |
| Training | $200-$500 | $2000-$5000 | 85-95% savings |
| Total TCO | $3300-$8800 | $10000-$29000 | 65-80% savings |
Application-Specific TCO Analysis
High-Speed Repetitive Applications
Pneumatic advantages multiply in rapid cycling:
- Cycle capability: 500-1000+ cycles per minute
- Maintenance intervals: Extended due to simple design
- Energy efficiency: Good for short-duration high-speed work
- Reliability factor: Fewer complex components to fail
Long-Stroke Positioning Applications
Rodless air cylinders excel in extended travel:
- Space efficiency: Compact installation compared to electric
- Force consistency: Uniform force throughout stroke length
- Speed capability: Faster than electric for equivalent stroke
- Cost scaling: Linear cost increase versus exponential for electric
Risk and Reliability Factors
Pneumatic Risk Assessment
Lower financial risk profile:
- Technology maturity: Proven technology with predictable costs
- Supplier stability: Multiple sources for components and service
- Obsolescence protection: Standard components remain available
- Skill availability: Widespread pneumatic expertise
Electric System Risk Factors
Higher financial uncertainty:
- Technology evolution: Rapid changes requiring updates and training
- Vendor dependence: Proprietary systems limit supplier options
- Obsolescence risk: Electronic components become unavailable
- Skill scarcity: Specialized expertise commands premium pricing
Return on Investment Calculations
Payback Period Analysis
Pneumatic systems show immediate advantages:
| Application Type | Pneumatic Payback | Electric Payback | Advantage Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple positioning | Immediate | 2-4 years | Continuous |
| High-speed cycling | 3-6 months | 1-3 years | Significant |
| Heavy-duty work | Immediate | 1-2 years | Substantial |
| Long-stroke motion | 6-12 months | 2-5 years | Major |
Financial Decision Framework
Cost Justification Guidelines
When electric actuators may justify higher costs:
- Precision requirements: Sub-millimeter positioning accuracy needed
- Complex motion: Multi-axis coordinated movement required
- Energy efficiency: Continuous duty with high energy costs
- Integration needs: Sophisticated control system requirements
Pneumatic Selection Criteria
Pneumatic cylinders provide optimal value when:
- Simple positioning: Two-position or basic motion requirements
- High-speed operation: Rapid cycling and fast response needed
- Cost sensitivity: Budget constraints or competitive pricing pressure
- Reliability priority: Minimal downtime and simple maintenance preferred
Strategic Cost Considerations
Long-Term Business Impact
Pneumatic systems support business objectives:
- Capital efficiency5: Lower investment requirements free capital for growth
- Operational flexibility: Simple systems adapt easily to changes
- Competitive advantage: Lower costs enable competitive pricing
- Risk management: Proven technology reduces operational uncertainty
Robert, who oversees automation investments for a German machinery manufacturer, conducted a comprehensive five-year analysis comparing pneumatic and electric solutions. His study showed pneumatic cylinders provided $180,000 in total savings across 50 actuators while delivering superior reliability and faster project completion times, leading to a company-wide standardization on Bepto pneumatic solutions.
Conclusion
Pneumatic cylinders deliver 60-80% lower total cost of ownership over five years compared to electric actuators, with substantial savings in initial purchase, installation, maintenance, and training costs outweighing most energy consumption differences.
FAQs About Cylinder vs Electric Actuator Costs
Q: Are pneumatic cylinders always less expensive than electric actuators initially?
Yes, pneumatic cylinders typically cost 50-75% less than equivalent electric actuators initially, with additional savings from simpler supporting components and installation requirements making the cost advantage even greater.
Q: How do energy costs compare between pneumatic and electric systems?
Electric actuators are more energy-efficient for continuous operation, but pneumatic cylinders often cost less overall due to their efficiency in intermittent high-speed applications and lower maintenance energy requirements.
Q: What hidden costs should I consider when comparing these technologies?
Electric actuators require expensive programming, specialized installation labor, ongoing training, and complex maintenance that can double or triple the total system cost compared to simple pneumatic cylinder installations.
Q: Do rodless cylinders offer better value than electric actuators for long-stroke applications?
Yes, rodless air cylinders typically provide 65-80% cost savings compared to electric actuators while offering faster speeds and simpler maintenance, making them superior value for most long-stroke positioning applications.
Q: How do maintenance costs differ between pneumatic and electric actuator systems?
Pneumatic cylinders require 60-80% lower annual maintenance costs due to simple seal replacement and basic air system service versus complex electronic diagnostics, motor service, and specialized programming support for electric systems.
-
Learn about Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), a financial estimate that helps assess the direct and indirect costs of a product over its entire life cycle. ↩
-
Learn about the design, types, and operational advantages of rodless air cylinders in industrial automation. ↩
-
Explore the operating principles of solenoid valves and how they are used to direct compressed air flow to control pneumatic actuators. ↩
-
Discover the concept of regenerative systems, which capture and reuse energy during deceleration, and their application in electric actuators. ↩
-
Understand capital efficiency, a key business metric that measures how effectively a company uses its financial resources to generate profits. ↩



