Many engineers struggle with inconsistent pneumatic cylinder speeds, jerky motion, and poor positioning accuracy, not realizing that selecting the wrong flow control valve type is costing them thousands in lost productivity and increased maintenance expenses.
Pneumatic flow control valves include needle valves for precise adjustment, ball valves for on/off control, proportional valves for automated systems, and specialized designs like butterfly and globe valves, each offering specific advantages for controlling air flow rates in rodless cylinders1 and other pneumatic applications.
Last week, I received a call from Sarah, a maintenance engineer at a Michigan automotive plant, whose rodless cylinder system was operating erratically with inconsistent speeds, causing $8,000 in daily production losses before we identified that her basic gate valves couldn’t provide the precise flow control her high-speed assembly line required.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Main Categories of Pneumatic Flow Control Valves?
- How Do Manual Flow Control Valves Compare in Performance and Applications?
- What Advantages Do Proportional Flow Control Valves Offer for Automated Systems?
- Which Flow Control Valve Type Should You Choose for Your Specific Application?
What Are the Main Categories of Pneumatic Flow Control Valves?
Understanding the different categories of pneumatic flow control valves is essential for optimizing your rodless cylinder performance and achieving the precise speed control your application demands.
Pneumatic flow control valves fall into four main categories: manual adjustment valves (needle, globe, ball), automated proportional valves, servo valves for high-precision applications, and specialized designs like butterfly valves for large flow applications, each designed for specific control requirements and performance levels.
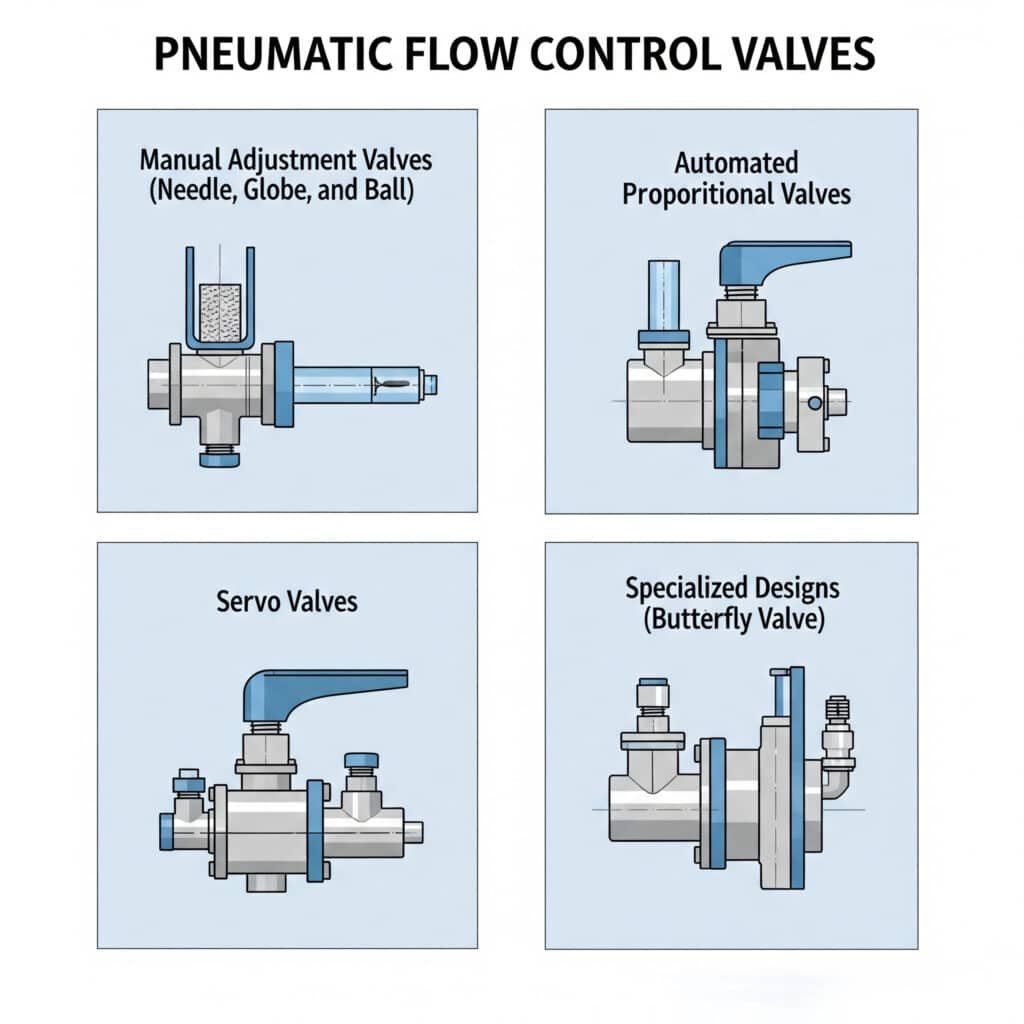
Manual Flow Control Valves
Manual flow control valves require operator adjustment and are ideal for applications where flow rates remain relatively constant. These valves offer cost-effective solutions for basic pneumatic systems.
Needle Valves provide the finest flow control adjustment through their tapered needle design. The precision threading allows for extremely small flow rate changes, making them perfect for applications requiring exact speed control in rodless cylinders.
Ball Valves offer quick quarter-turn operation for on/off control applications. While they don’t provide variable flow control, they excel in isolation service and emergency shutdown applications where tight sealing is critical.
Globe Valves feature excellent throttling characteristics with their plug-and-seat design. They provide good flow control throughout their operating range and are suitable for frequent operation in moderate-pressure applications.
Automated Flow Control Valves
Automated valves respond to electrical signals, enabling remote control and integration with modern control systems. These valves are essential for automated production lines and precision applications.
Proportional Valves convert electrical signals (typically 4-20mA) into precise flow control. They offer excellent repeatability and can be integrated with PLC systems for automated pneumatic cylinder speed control.
Servo Valves represent the highest level of flow control precision, featuring closed-loop feedback systems and response times under 10 milliseconds. These valves are essential for high-speed, high-precision applications.
Specialized Flow Control Designs
| Valve Type | Flow Capacity | Control Precision | Typical Applications | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Needle Valve | Low-Medium | Excellent | Precision adjustment | Low |
| Ball Valve | High | On/Off Only | Isolation service | Low |
| Butterfly Valve | Very High | Good | Large pipe applications | Medium |
| Proportional Valve | Medium-High | Very Good | Automated systems | High |
| Servo Valve | Medium | Excellent | High-precision control | Very High |
At Bepto, we help customers select the optimal flow control valve type for their rodless cylinder applications, ensuring maximum performance while minimizing costs through our extensive experience with pneumatic system optimization.
How Do Manual Flow Control Valves Compare in Performance and Applications?
Manual flow control valves offer different performance characteristics and are suited for specific applications where operator control and cost-effectiveness are primary considerations.
Manual flow control valves provide reliable, cost-effective flow regulation with needle valves offering the highest precision (±1% flow control), ball valves providing excellent sealing for on/off applications, and globe valves delivering good throttling performance for general industrial use.

Needle Valve Performance Characteristics
Needle valves excel in applications requiring precise flow adjustment. Their tapered needle design allows for extremely fine flow control, making them ideal for rodless cylinder speed adjustment where consistent, repeatable motion is critical.
The multi-turn operation of needle valves provides excellent resolution – typically requiring 10-15 turns from fully closed to fully open. This gives operators precise control over flow rates, with typical adjustment resolution of 0.1% of full flow.
Installation Considerations:
- Install with flow direction under the seat for better control
- Provide adequate clearance for manual adjustment
- Consider accessibility for routine maintenance
- Use appropriate thread sealant for pneumatic applications
Ball Valve Applications
Ball valves serve as excellent isolation valves in pneumatic systems, providing bubble-tight shutoff when properly installed. While they don’t offer variable flow control, their quarter-turn operation makes them ideal for emergency shutdown applications.
In rodless cylinder systems, ball valves are commonly used for:
- Main air supply isolation
- System section isolation for maintenance
- Emergency stop applications
- Branch line control
Globe Valve Characteristics
Globe valves provide good throttling2 control with their linear flow characteristics. The plug-and-seat design offers predictable flow curves, making them suitable for applications where moderate flow control precision is acceptable.
Performance Comparison:
| Valve Feature | Needle Valve | Ball Valve | Globe Valve |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Control Range | 100:1 | On/Off Only | 50:1 |
| Adjustment Resolution | Excellent | N/A | Good |
| Pressure Drop | Moderate | Very Low | High |
| Maintenance Requirements | Low | Very Low | Moderate |
Michael, a plant engineer from a Texas packaging facility, switched from globe valves to our recommended needle valves for his rodless cylinder speed control. “The precision improvement was immediate,” he told me. “We went from ±5% speed variation to ±1%, which eliminated our product positioning problems and saved us $12,000 monthly in rejected packages.”
What Advantages Do Proportional Flow Control Valves Offer for Automated Systems?
Proportional flow control valves provide electrically controlled, continuously variable flow regulation that enables precise automation and integration with modern control systems.
Proportional flow control valves offer remote control capability, precise flow regulation (±0.5% accuracy), fast response times (10-50ms), and seamless PLC integration, making them essential for automated rodless cylinder applications requiring consistent performance and programmable operation.

Electronic Control Capabilities
Proportional valves convert electrical signals into precise mechanical flow control. Standard input signals include 4-20mA current loops3 and 0-10VDC voltage signals, providing excellent compatibility with industrial control systems.
The electronic control offers several key advantages:
- Remote Operation: Control valves from central locations
- Programmable Settings: Store multiple flow rate profiles
- Automatic Adjustment: Respond to changing system demands
- Data Integration: Monitor performance and log operational data
Performance Specifications
Modern proportional valves deliver exceptional performance characteristics that manual valves cannot match:
Response Time: 10-50 milliseconds typical, enabling rapid system response
Resolution: 0.1-1% of full scale, providing precise flow control
Repeatability: ±0.5% typical, ensuring consistent operation
Linearity: ±2% of full scale, predictable flow characteristics
System Integration Benefits
Proportional valves integrate seamlessly with modern automation systems, providing capabilities that transform pneumatic system performance:
| Integration Feature | Manual Valves | Proportional Valves | Performance Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Control | Not Available | Standard Feature | Centralized operation |
| Programmable Settings | Manual Only | Multiple Profiles | Flexible operation |
| Feedback Control | Not Available | Closed-loop Capable | Precise positioning |
| Diagnostic Capability | Visual Only | Electronic Monitoring | Predictive maintenance |
Energy Efficiency Advantages
Proportional valves optimize energy consumption by providing only the flow rate needed for each application phase. This demand-based control typically reduces compressed air consumption by 20-40% compared to fixed-setting manual valves.
The valves can automatically adjust flow rates based on:
- Load requirements
- Cycle phase
- System pressure
- Temperature conditions
Lisa, who manages automation at a German automotive parts manufacturer, implemented our proportional valve recommendations for her rodless cylinder assembly stations. “The integration with our PLC system4 was seamless,” she explained. “We achieved ±0.1mm positioning accuracy and reduced our air consumption by 35%, paying for the valve upgrade in just eight months through energy savings alone.”
Which Flow Control Valve Type Should You Choose for Your Specific Application?
Selecting the right flow control valve requires careful analysis of your application requirements, performance needs, and budget considerations to ensure optimal system performance.
Flow control valve selection depends on precision requirements (needle valves for ±1% control, proportional valves for automated systems), flow capacity needs (butterfly valves for high flow, needle valves for low flow), and integration requirements (manual valves for simple systems, proportional valves for automation).
Application Requirements Analysis
The first step in valve selection involves analyzing your specific application requirements:
Flow Rate Requirements: Calculate peak flow demand based on your rodless cylinder specifications and cycle rates. Include safety factors for future expansion or unexpected demand spikes.
Control Precision Needs: Determine acceptable speed variation tolerances. High-precision applications may require proportional or servo valves, while general industrial applications may work well with needle valves.
Environmental Conditions: Consider operating temperature, contamination levels, and space constraints that may affect valve selection and installation.
Performance vs. Cost Analysis
Different valve types offer varying performance levels at different cost points:
| Valve Type | Initial Cost | Performance Level | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Needle Valve | $50-200 | High Precision | Manual adjustment systems |
| Ball Valve | $30-150 | On/Off Only | Isolation applications |
| Globe Valve | $75-300 | Moderate Control | General throttling |
| Proportional Valve | $500-2000 | Very High | Automated systems |
| Servo Valve | $2000-8000 | Excellent | Critical precision applications |
Selection Decision Matrix
Use this systematic approach to select the optimal valve type:
Step 1: Define Requirements
- Maximum and minimum flow rates
- Required control precision
- Response time needs
- Integration requirements
Step 2: Evaluate Options
- Compare valve types against requirements
- Consider total cost of ownership5
- Assess installation complexity
- Review maintenance requirements
Step 3: Make Selection
- Choose valve type that best meets requirements
- Select appropriate size and specifications
- Plan installation and integration approach
Integration and Installation Considerations
Proper valve integration ensures optimal performance:
Manual Valves: Provide adequate access for adjustment and maintenance. Consider operator training requirements and establish adjustment procedures.
Proportional Valves: Plan electrical connections and control system integration. Ensure adequate power supply and signal conditioning equipment.
System Design: Consider valve placement, piping design, and maintenance access. Plan for future expansion and modification needs.
At Bepto, we provide comprehensive valve selection support for our customers’ rodless cylinder applications. Our engineering team analyzes your specific requirements and recommends the optimal valve solution that balances performance, cost, and reliability for your unique application needs.
Conclusion
Selecting the right pneumatic flow control valve type is crucial for achieving optimal rodless cylinder performance, with needle valves excelling in precision applications, proportional valves enabling automation, and specialized designs serving specific industrial requirements.
FAQs About Pneumatic Flow control valves
Q: What’s the difference between needle valves and proportional valves for rodless cylinder control?
Needle valves provide manual precision adjustment with excellent flow control (±1%) at low cost, while proportional valves offer electrical control, automation capability, and faster response times (10-50ms) but at higher initial cost ($500-2000 vs $50-200).
Q: Can I use ball valves for speed control in pneumatic cylinders?
Ball valves are designed for on/off control only and cannot provide variable speed control for pneumatic cylinders; use needle valves for manual speed adjustment or proportional valves for automated speed control applications.
Q: How do I determine the right size flow control valve for my rodless cylinder?
Calculate your cylinder’s air consumption (bore area × stroke × cycle rate), add a 20-30% safety factor, and select a valve with flow capacity 1.5 times your calculated requirement to ensure adequate performance without excessive pressure drop.
Q: What maintenance do pneumatic flow control valves require?
Manual valves need quarterly inspection and annual lubrication, while proportional valves require monthly electronic calibration checks, annual seal replacement, and regular cleaning of electrical connections for optimal performance.
Q: Are proportional flow control valves worth the higher cost for automated systems?
Yes, proportional valves typically pay for themselves within 6-18 months through improved productivity (20-40% faster cycles), reduced air consumption (20-35% savings), and eliminated manual adjustment labor costs in automated applications.
-
Learn about the design, types, and operational advantages of rodless pneumatic cylinders in industrial automation. ↩
-
Explore the principle of throttling and how certain valves are designed to regulate the pressure and flow of a fluid. ↩
-
Understand the 4-20mA current loop, a common and robust industry standard for analog control signals in industrial instrumentation. ↩
-
Discover what a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is and its fundamental role in controlling machinery and processes in automation. ↩
-
Learn about Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), a financial estimate that helps assess the direct and indirect costs of a product over its life cycle. ↩



