Engineers waste countless hours designing custom pneumatic circuits from scratch, creating complex manifolds and struggling with reliability issues that could be eliminated through modular valve systems. Traditional circuit design approaches lead to maintenance nightmares, difficult troubleshooting, and expensive custom components that delay projects and increase costs. 🔧
Modular valve systems enable reliable pneumatic circuit construction through standardized components, simplified maintenance, reduced leak points, and flexible configuration options that streamline design, installation, and service while improving overall system reliability. This approach transforms pneumatic circuit design from custom engineering to systematic assembly.
Yesterday, I spoke with Carlos, a design engineer at a Florida automation company, whose team was spending 3 weeks designing each custom pneumatic circuit when modular solutions could reduce this to 3 days.
Table of Contents
- What Are Modular Pneumatic Valve Systems and Their Key Advantages?
- How Do You Design Circuits Using Modular Valve Building Blocks?
- Which Configuration Strategies Maximize Modular System Reliability?
- What Maintenance and Troubleshooting Benefits Do Modular Systems Provide?
What Are Modular Pneumatic Valve Systems and Their Key Advantages?
Understanding modular valve architecture is essential for modern pneumatic circuit design. 🏗️
Modular pneumatic valve systems use standardized valve blocks, manifolds, and connection interfaces that snap together to create complete circuits, eliminating custom machining, reducing assembly time, and providing unlimited configuration flexibility through interchangeable components. This building-block approach revolutionizes pneumatic system design and maintenance.
Modular System Architecture
Standardized Building Blocks
Modular systems consist of:
- Base manifolds providing air supply and exhaust connections
- Valve blocks containing directional control, flow control, and pressure regulation
- End plates sealing the manifold assembly
- Interface modules connecting to actuators and sensors
Universal Connection Standards
All components use standardized interfaces ensuring perfect fit and eliminating compatibility issues between manufacturers following industry standards.
Scalable Configuration
Systems can be easily expanded or reconfigured by adding or removing valve blocks without affecting other circuit functions.
Modular vs. Traditional Circuit Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Custom | Modular Systems | Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design Time | 2-4 weeks | 2-4 days | 85% reduction |
| Assembly Time | 8-16 hours | 2-4 hours | 75% reduction |
| Leak Points | 20-40 per circuit | 4-8 per circuit | 70% reduction |
| Maintenance Access | Poor | Excellent | Significant |
| Configuration Changes | Major rework | Simple reconfiguration | Revolutionary |
How Do You Design Circuits Using Modular Valve Building Blocks?
Systematic modular design approaches ensure optimal circuit performance and reliability. 📋
Effective modular circuit design follows a structured process: analyze actuator requirements, select appropriate valve functions, arrange modules for optimal flow paths, and configure control interfaces to create efficient, maintainable pneumatic circuits. Our proven design methodology eliminates guesswork and ensures first-time success.
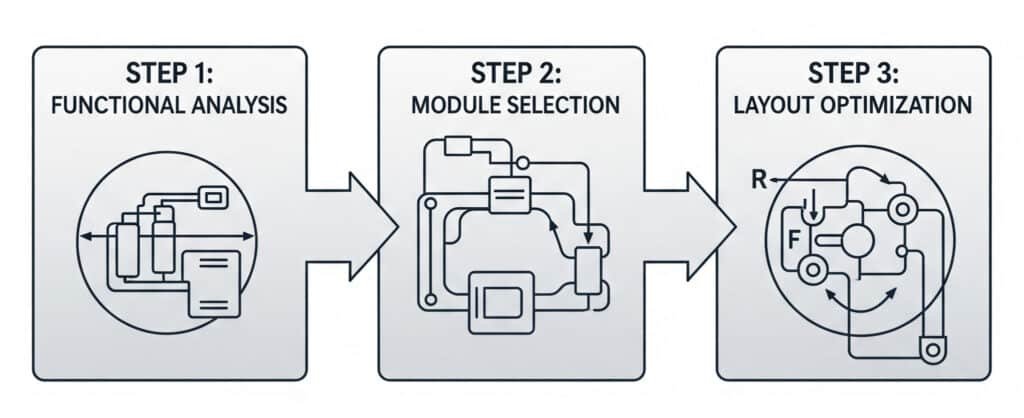
Bepto Modular Design Process
At Bepto, we’ve developed a systematic approach for modular circuit design:
Step 1: Functional Analysis
- Identify all actuators and their operating requirements
- Determine control logic and sequencing needs
- Specify safety and emergency stop requirements
- Calculate total air consumption and pressure needs
Step 2: Module Selection
- Choose appropriate valve types for each function
- Select flow control and pressure regulation modules
- Determine manifold size and configuration
- Specify control interface requirements
Step 3: Layout Optimization
- Arrange modules for shortest flow paths
- Minimize pressure drops and dead volumes
- Ensure easy access for maintenance
- Plan cable routing and connection points
Common Circuit Building Blocks
| Function | Module Type | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Directional Control | 5/2, 5/3, 3/2 valves | Cylinder control, air routing |
| Flow Control | Adjustable restrictors | Speed control, soft start |
| Pressure Control | Regulators, relief valves | Force control, safety |
| Logic Functions | AND, OR, NOT modules | Sequence control, interlocks |
| Interface | I/O modules, pilot valves | PLC connection, manual control |
Design Example: Dual Cylinder System
Carlos’s team needed to control two cylinders with independent speed control and synchronized operation:
Required Components:
- Base manifold (6-station)
- Two 5/2 directional control valves
- Two flow control modules
- One pressure regulator module
- One logic AND module
- End plate assembly
Configuration Benefits:
- 60% fewer connections than traditional approach
- Single air supply connection
- Integrated speed control
- Easy logic modification
- Compact 12″ × 4″ footprint
Which Configuration Strategies Maximize Modular System Reliability?
Strategic configuration choices significantly impact long-term system reliability and performance. 🛡️
Maximizing modular system reliability requires proper manifold sizing, strategic redundancy implementation, optimal module arrangement, and systematic pressure management to prevent failures and ensure consistent operation under varying conditions. These strategies prevent common failure modes and extend system life.
Critical Reliability Strategies
Manifold Sizing for Future Expansion
Size manifolds 25-30% larger than immediate needs to accommodate future additions without system redesign. This prevents costly retrofits and maintains optimal flow characteristics.
Strategic Redundancy Implementation
For critical applications, implement redundant control paths:
- Duplicate safety functions
- Backup pressure regulation
- Alternative control signal paths
- Emergency manual overrides
Pressure Management Optimization
Proper pressure distribution prevents cascading failures:
- Dedicated regulators for critical functions
- Pressure monitoring at key points
- Relief valve protection for sensitive components
- Staged pressure reduction for complex circuits
Bepto Reliability Enhancement Features
| Feature | Benefit | Reliability Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| O-ring Face Seals1 | Eliminates leak paths | 95% leak reduction |
| Captive Fasteners | Prevents lost hardware | 100% retention |
| Color-coded Modules | Reduces wiring errors | 80% error reduction |
| Status Indicators | Visual system health | 60% faster diagnosis |
| Modular Diagnostics | Individual function testing | 70% troubleshooting improvement |
Environmental Considerations
Temperature Management
Modular systems handle temperature variations better than custom circuits due to:
- Uniform thermal expansion characteristics
- Standardized seal materials
- Consistent mounting interfaces
- Integrated thermal protection
Contamination Protection
Enhanced contamination resistance through:
- Sealed module interfaces
- Protected connection points
- Easy filter integration
- Simplified cleaning access
Configuration Best Practices
Maria, a maintenance supervisor from a Texas manufacturing plant, implemented our modular reliability strategies and reduced her pneumatic system downtime by 75% while cutting maintenance costs in half.
What Maintenance and Troubleshooting Benefits Do Modular Systems Provide?
Modular systems dramatically simplify maintenance and troubleshooting compared to traditional pneumatic circuits. 🔍
Modular pneumatic systems enable rapid fault isolation, individual component replacement, simplified spare parts inventory, and reduced maintenance training requirements through standardized interfaces and plug-and-play functionality. These advantages translate to significant operational cost savings and improved uptime.
Maintenance Advantages
Individual Component Access
Each valve function can be serviced independently without affecting other circuit operations:
- Remove single modules for repair or replacement
- Test individual functions in isolation
- Perform preventive maintenance on schedule
- Upgrade specific functions without system shutdown
Standardized Spare Parts
Modular systems require fewer unique spare parts:
- Common valve blocks across multiple circuits
- Standardized seals and wear components
- Interchangeable modules between applications
- Reduced inventory investment and storage space
Simplified Training Requirements
Maintenance technicians learn one modular system instead of multiple custom designs:
- Standard troubleshooting procedures
- Common repair techniques
- Universal diagnostic methods
- Transferable skills across applications
Troubleshooting Capabilities
| Diagnostic Feature | Traditional Circuit | Modular System | Time Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fault Isolation | 2-4 hours | 15-30 minutes | 85% reduction |
| Component Testing | Difficult/impossible | Individual module test | Revolutionary |
| Visual Status | Limited indicators | LED status per module | Immediate |
| Documentation | Custom drawings | Standard schematics | 70% faster |
Predictive Maintenance Integration
Built-in Diagnostics
Modern modular systems include diagnostic capabilities:
- Cycle counters2 for wear prediction
- Pressure monitoring for performance trends
- Temperature sensors for thermal management
- Vibration detection for mechanical issues
Remote Monitoring
Modular systems integrate easily with Industry 4.03 initiatives:
- Individual module status reporting
- Performance data collection
- Predictive failure algorithms
- Automated maintenance scheduling
Real-World Maintenance Results
David, a plant engineer from a Michigan automotive facility, tracked maintenance metrics after converting to modular systems:
Before Modular Systems:
- Average repair time: 4.5 hours
- Spare parts inventory: $45,000
- Training time per technician: 40 hours
- Annual maintenance cost: $180,000
After Modular Implementation:
- Average repair time: 45 minutes
- Spare parts inventory: $18,000
- Training time per technician: 12 hours
- Annual maintenance cost: $65,000
Results: 64% reduction in maintenance costs and 85% improvement in repair times.
Emergency Response Benefits
Rapid Component Replacement
Critical system failures can be resolved quickly:
- Keep pre-configured spare modules in stock
- Swap modules in minutes, not hours
- Restore production immediately
- Repair failed modules offline
Temporary Configuration Changes
Modular systems enable quick process modifications:
- Add temporary bypass functions
- Implement emergency operating modes
- Reconfigure for reduced capacity operation
- Maintain production during repairs
Conclusion
Modular pneumatic valve systems revolutionize circuit design and maintenance through standardized components, simplified assembly, enhanced reliability, and dramatically reduced service requirements, making them essential for modern industrial automation.
FAQs About Modular Pneumatic Valve Systems
Q: Are modular valve systems more expensive than traditional custom circuits?
A: While initial component costs may be 10-20% higher, modular systems provide 40-60% total cost savings through reduced design time, faster assembly, lower maintenance costs, and improved reliability over the system lifecycle.
Q: Can existing pneumatic circuits be converted to modular systems?
A: Yes, most existing circuits can be converted to modular systems during planned maintenance or upgrades. The conversion process typically pays for itself within 6-12 months through reduced maintenance and improved reliability.
Q: Do modular systems work with different actuator types and sizes?
A: Modular systems work with all standard pneumatic actuators including cylinders, rotary actuators, grippers, and rodless cylinders. The standardized interfaces accommodate various actuator connection requirements through appropriate interface modules.
Q: How do modular systems handle high-flow applications?
A: Bepto modular systems accommodate high-flow requirements through larger manifold sizes, parallel valve configurations, and high-capacity valve blocks. Flow rates up to 200 SCFM per circuit are readily achievable with proper configuration.
Q: What training is required for technicians working with modular systems?
A: Technicians typically require 1-2 days of training to understand modular system principles and maintenance procedures, compared to weeks of training for multiple custom circuit designs. The standardized approach significantly reduces learning curves and improves troubleshooting efficiency.
-
Discover how O-ring face seal fittings provide a highly reliable, leak-free connection in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. ↩
-
Learn how cycle counters are used to monitor equipment usage and predict maintenance needs based on operational life. ↩
-
Explore the key concepts of the fourth industrial revolution, including IoT, smart factories, and data-driven manufacturing. ↩




