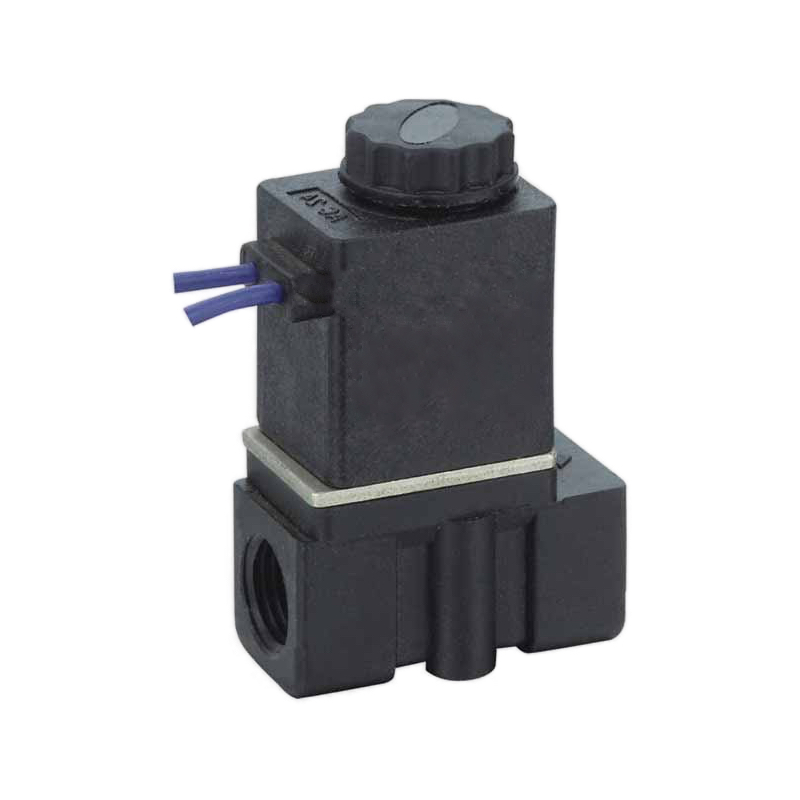
Solenoid valve failures cause unexpected production shutdowns, erratic cylinder operation, and costly emergency repairs. Many maintenance teams struggle with systematic troubleshooting, leading to unnecessary part replacements and extended downtime that could be avoided with proper diagnostic procedures.
Troubleshooting failing pneumatic solenoid valves1 involves systematic electrical testing, air flow verification, mechanical inspection, and performance analysis to identify root causes including coil failures, contamination buildup, mechanical wear, and electrical connection problems for efficient repair and prevention strategies. ⚡
This morning, Jennifer, a maintenance technician at a food processing plant in Texas, saved her facility $3,000 in emergency repairs by correctly diagnosing a simple electrical connection issue that was causing intermittent valve operation.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Most Common Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Failure Modes?
- How Do You Systematically Diagnose Solenoid Valve Problems?
- Which Tools and Tests Are Essential for Solenoid Valve Troubleshooting?
- What Preventive Measures Can Extend Solenoid Valve Service Life?
What Are the Most Common Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Failure Modes?
Understanding typical failure patterns helps maintenance teams quickly identify problems and implement appropriate solutions.
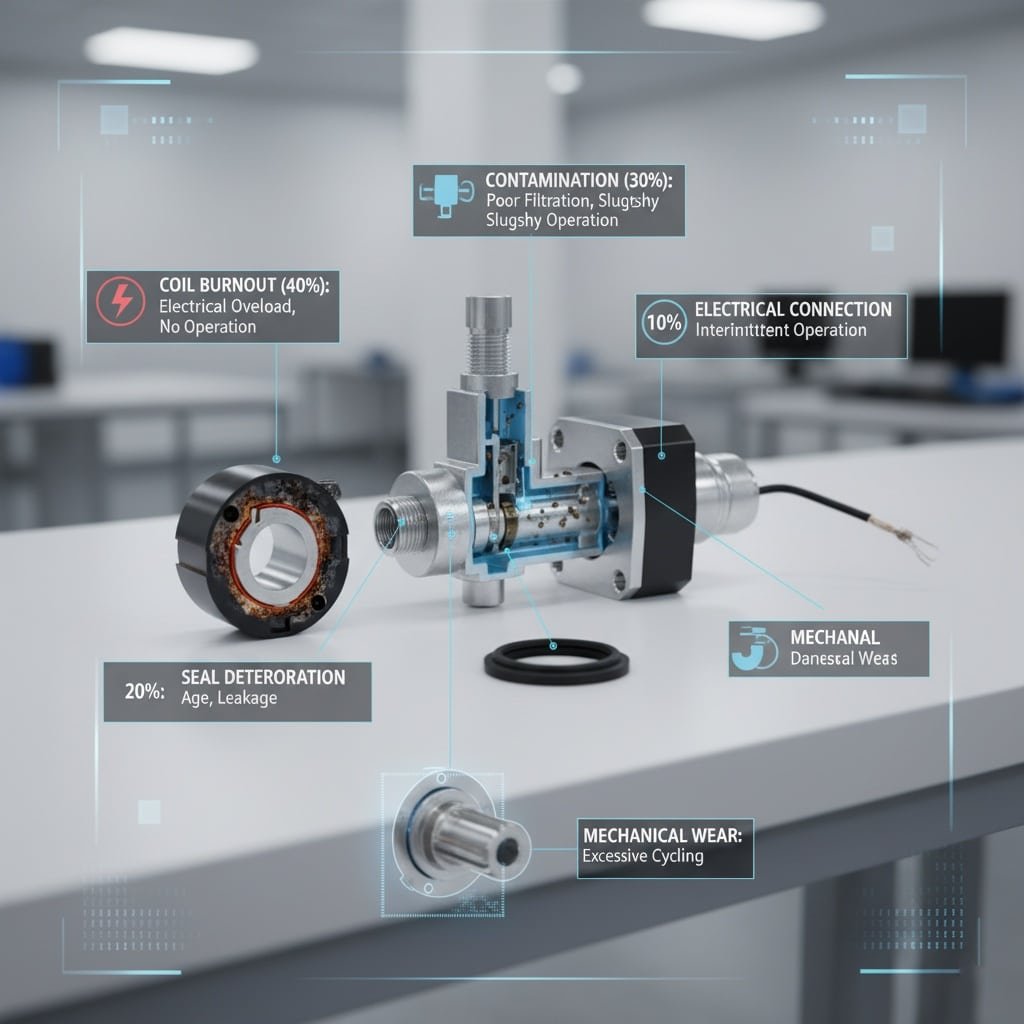
Common pneumatic solenoid valve failure modes include coil burnout from electrical overload, contamination causing mechanical binding, seal deterioration leading to internal leakage, electrical connection failures creating intermittent operation, and mechanical wear from excessive cycling or improper installation conditions.
Electrical Failures
Coil burnout represents 40% of solenoid valve failures, typically caused by voltage spikes, overheating, or moisture infiltration. Burned coils show characteristic discoloration and insulation breakdown that’s easily identified during inspection.
Contamination Problems
Dirt, oil, and moisture contamination cause 30% of valve failures by preventing proper spool movement or creating seal damage. Our Bepto solenoid valves include advanced filtration and moisture protection to minimize these issues.
Mechanical Wear Issues
Excessive cycling, improper pressure levels, or inadequate lubrication cause mechanical component wear that results in sluggish operation or complete failure to actuate.
Common Failure Analysis
| Failure Mode | Frequency | Primary Causes | Typical Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coil Burnout | 40% | Electrical overload | No operation, hot coil |
| Contamination | 30% | Poor filtration | Sluggish, erratic operation |
| Seal Failure | 20% | Age, temperature | Internal leakage |
| Connection Issues | 10% | Vibration, corrosion | Intermittent operation |
Environmental Factors
Temperature extremes, vibration, and corrosive atmospheres accelerate valve degradation. Proper environmental protection extends service life significantly and reduces failure frequency.
Installation-Related Failures
Improper mounting, incorrect pressure settings, or inadequate electrical connections cause premature failures that proper installation procedures can prevent.
Age-Related Degradation
Even properly maintained valves eventually experience seal hardening, spring fatigue, and electrical insulation breakdown that requires replacement after 5-10 years of service.
Jennifer’s Texas food plant discovered that 70% of their valve failures were contamination-related, leading to improved filtration systems that reduced failure rates by 60%. 🏭
How Do You Systematically Diagnose Solenoid Valve Problems?
Effective troubleshooting follows a logical sequence that quickly isolates problems without unnecessary component replacement.
Systematic solenoid valve diagnosis involves visual inspection for obvious damage, electrical testing of coil resistance and voltage supply, air flow verification through the valve body, mechanical operation testing, and performance measurement to identify specific failure modes and root causes efficiently.
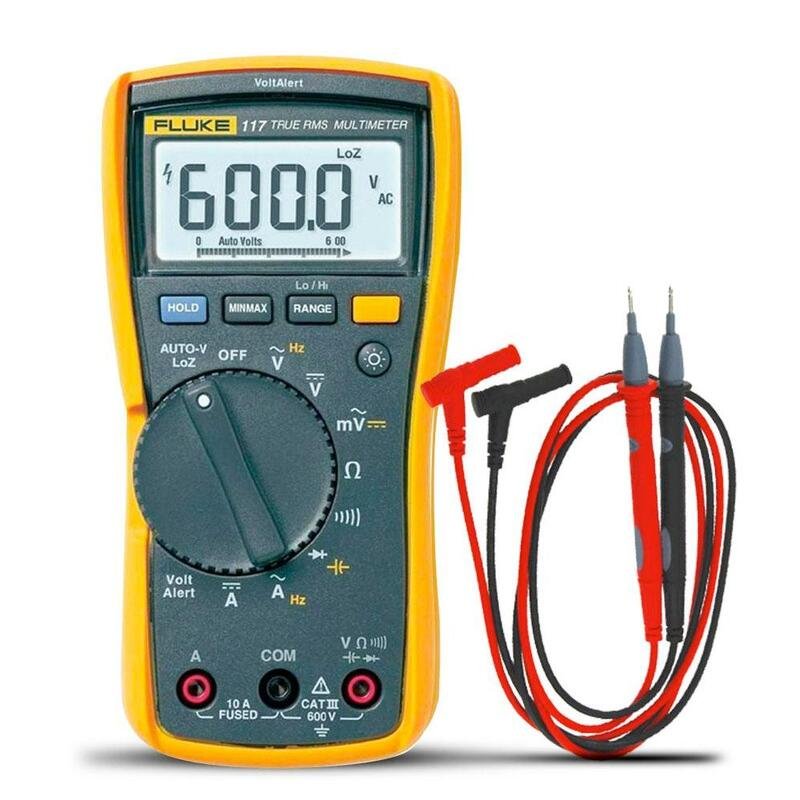

Initial Visual Inspection
Start with visual examination for obvious damage including burned coils, damaged connectors, contamination buildup, or mechanical damage. Many problems are immediately apparent during careful visual inspection.
Electrical System Testing
Test coil resistance with a multimeter2 – normal values typically range from 10-200 ohms depending on valve design. Infinite resistance indicates open coil while zero resistance suggests short circuit.
Power Supply Verification
Verify correct voltage and current supply to the valve coil. Voltage variations beyond ±10% of rated values can cause erratic operation or premature failure.
Diagnostic Sequence
| Step | Test Method | Normal Result | Problem Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual | Inspection | Clean, undamaged | Burns, contamination |
| Electrical | Multimeter | Rated resistance | Open/short circuit |
| Power | Voltage test | Rated voltage ±10% | Over/under voltage |
| Mechanical | Manual operation | Smooth movement | Binding, sluggish |
Air Flow Testing
With electrical power confirmed, test air flow through the valve in both positions. Proper flow indicates mechanical function while restricted flow suggests contamination or wear.
Performance Measurement
Measure response time, flow capacity, and leakage rates to quantify valve performance against specifications. This data helps determine if repair or replacement is most cost-effective.
Root Cause Analysis
Document findings to identify patterns that indicate systemic problems requiring broader corrective action beyond individual valve repair or replacement.
Which Tools and Tests Are Essential for Solenoid Valve Troubleshooting?
Proper diagnostic tools enable accurate problem identification and efficient repair without guesswork or unnecessary part replacement.
Essential solenoid valve troubleshooting tools include digital multimeters for electrical testing, pressure gauges for system verification, flow meters for performance measurement, insulation testers for coil evaluation, and basic hand tools for disassembly and mechanical inspection of valve components.
Electrical Testing Equipment
Digital multimeters measure coil resistance, voltage supply, and current draw. Insulation testers3 verify coil-to-ground resistance to detect insulation breakdown that could cause safety hazards or erratic operation.
Pneumatic Testing Tools
Pressure gauges verify system pressure and pressure drop across valves. Flow meters measure actual flow capacity compared to specifications to identify performance degradation.
Mechanical Inspection Tools
Basic hand tools for valve disassembly, inspection mirrors for internal examination, and cleaning supplies for contamination removal are essential for thorough mechanical evaluation.
Essential Tool Kit
| Tool Category | Specific Tools | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical | Digital multimeter, insulation tester | Coil and wiring testing |
| Pneumatic | Pressure gauges, flow meters | System performance |
| Mechanical | Hand tools, inspection mirrors | Physical examination |
| Cleaning | Solvents, brushes, compressed air | Contamination removal |
Diagnostic Software
Advanced facilities use diagnostic software that interfaces with smart valves to provide detailed performance data and trend analysis for predictive maintenance scheduling.
Safety Equipment
Proper safety equipment including lockout/tagout4 devices, safety glasses, and electrical safety gear is essential for safe troubleshooting procedures.
Documentation Tools
Cameras for recording problem conditions, maintenance logs for tracking patterns, and diagnostic worksheets ensure thorough documentation for future reference and trend analysis.
Calibration Requirements
Test equipment requires regular calibration to ensure accurate measurements. Our Bepto service team provides calibration services and training for optimal diagnostic accuracy.
What Preventive Measures Can Extend Solenoid Valve Service Life?
Proactive maintenance significantly extends valve life while reducing unexpected failures and associated downtime costs.
Preventive measures extending solenoid valve service life include regular cleaning and contamination control, proper electrical connection maintenance, environmental protection, scheduled lubrication, performance monitoring, and replacement of wear components before failure occurs to maximize reliability and minimize costs.
Contamination Control
Install proper filtration, maintain clean air supply, and regularly clean valve exteriors to prevent contamination buildup. Clean valves operate more reliably and last significantly longer than contaminated units.
Electrical Maintenance
Inspect and tighten electrical connections quarterly, protect connections from moisture and corrosion, and verify proper voltage supply to prevent electrical failures.
Environmental Protection
Use appropriate enclosures for harsh environments, maintain proper operating temperatures, and protect valves from vibration and mechanical damage that accelerate wear.
Preventive Maintenance Schedule
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Expected Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | Early problem detection |
| Electrical Testing | Quarterly | Prevent electrical failures |
| Contamination Cleaning | Quarterly | Extend mechanical life |
| Performance Testing | Semi-annually | Optimize operation |
Lubrication Programs
Follow manufacturer lubrication schedules using approved lubricants. Proper lubrication reduces mechanical wear and extends service life by 50-100% in many applications.
Performance Monitoring
Track valve response times, flow rates, and cycle counts to identify gradual degradation before complete failure occurs. This data enables planned replacement during scheduled maintenance windows.
Spare Parts Management
Maintain appropriate spare parts inventory including coils, seals, and complete valve assemblies for critical applications to minimize downtime during failures.
Training Programs
Train maintenance staff on proper troubleshooting procedures, safety requirements, and preventive maintenance techniques to ensure consistent, effective valve care throughout the facility.
Systematic solenoid valve troubleshooting transforms reactive maintenance into proactive reliability management that maximizes uptime and minimizes costs. 🔧
FAQs About Troubleshooting Pneumatic Solenoid Valves
Q: How can I tell if a solenoid valve coil is burned out without removing it from the system?
A: Test coil resistance with a multimeter across the electrical terminals. Normal coils show resistance values between 10-200 ohms (check manufacturer specifications). Infinite resistance indicates an open (burned) coil, while zero resistance suggests a short circuit. Also check for physical signs like discoloration, burning smell, or excessive heat.
Q: What causes solenoid valves to operate intermittently, and how do I fix it?
A: Intermittent operation typically results from loose electrical connections, voltage fluctuations, or contamination causing mechanical binding. Check all electrical connections for tightness and corrosion, verify stable voltage supply within ±10% of rated voltage, and inspect for contamination buildup that might cause sluggish operation.
Q: Can I repair a solenoid valve myself, or should I always replace it?
A: Simple repairs like cleaning contamination, tightening connections, or replacing seals can often be performed in-house with proper tools and training. However, coil replacement or major mechanical repairs often require specialized knowledge and tools. Consider replacement if repair costs exceed 60-70% of new valve cost.
Q: How do I determine if the problem is with the solenoid valve or elsewhere in the pneumatic system?
A: Isolate the valve by testing it independently. Manually actuate the valve (if equipped with manual override) to verify mechanical function, then test electrical operation. If the valve operates properly in isolation but fails in the system, look for pressure, flow, or control signal problems elsewhere in the circuit.
Q: What are the warning signs that a solenoid valve is about to fail?
A: Early warning signs include slower response times, reduced flow capacity, unusual noises during operation, increased operating temperature, intermittent operation, and visible contamination or damage. Regular performance monitoring can detect these signs before complete failure occurs, allowing planned replacement during scheduled maintenance.
-
Learn the basic principle of how an electric current creates a magnetic field to move a plunger and actuate a pneumatic valve. ↩
-
Review a practical guide on using a digital multimeter to measure voltage, current, and resistance in electrical circuits. ↩
-
Understand the function of an insulation resistance tester (or Megohmmeter) and how it’s used to check the integrity of electrical insulation. ↩
-
Learn about the official Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) safety procedures for controlling hazardous energy during equipment service and maintenance. ↩



