Is your pneumatic system performing sluggishly with erratic cycle times? 😰 Clogged silencers create dangerous back pressure1 that damages valves, reduces cylinder force, and causes premature component failure. Without proper exhaust flow, your entire automation system becomes unreliable and costly to maintain.
Silencer clogging significantly reduces pneumatic system performance by creating back pressure that slows cylinder speeds, decreases force output, causes valve hunting2, and leads to overheating in rodless cylinders and other pneumatic components, ultimately resulting in system instability and premature equipment failure.
Last month, I helped David, a maintenance engineer at an automotive parts facility in Detroit, whose production line was experiencing 40% slower cycle times and frequent valve malfunctions due to severely clogged exhaust silencers.
Table of Contents
- How Does Silencer Clogging Affect Cylinder Speed and Force Output?
- What Are the Warning Signs of Silencer Blockage in Pneumatic Systems?
- How Can Clogged Silencers Damage Valves and Control Components?
- What Maintenance Practices Prevent Silencer Clogging Issues?
How Does Silencer Clogging Affect Cylinder Speed and Force Output?
Restricted exhaust flow creates cascading performance problems throughout your pneumatic system. 🔧
Clogged silencers reduce cylinder speed by 30-50% and decrease force output by up to 25% due to back pressure buildup, which prevents complete air evacuation during exhaust cycles and creates resistance against piston movement in rodless cylinders and standard pneumatic actuators.
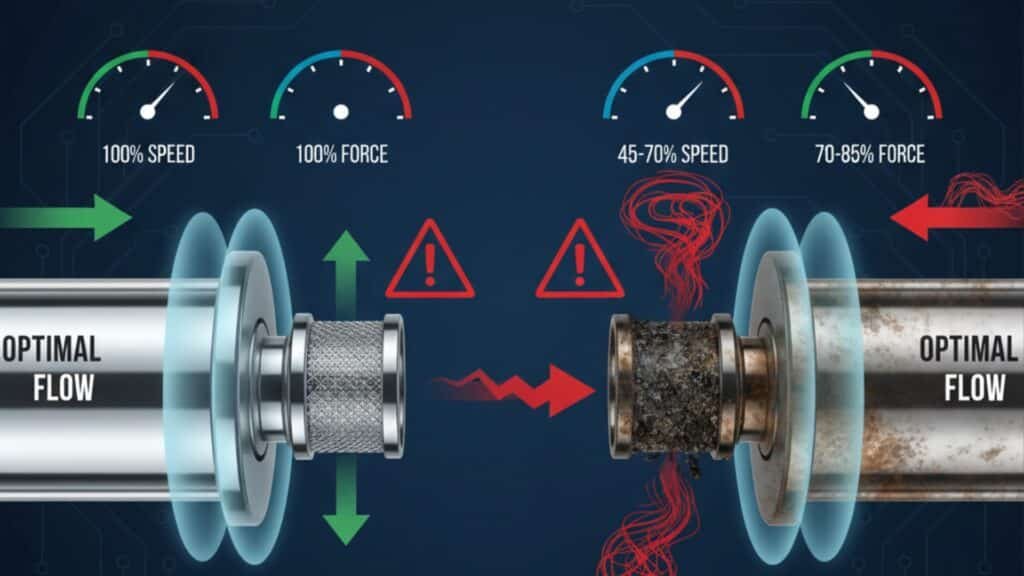

Performance Impact Analysis
Speed Reduction Mechanisms
- Exhaust restriction: Trapped air slows piston retraction
- Pressure differential3: Reduced pressure gradient across cylinder
- Flow limitation: Restricted orifice area reduces evacuation rate
- System resistance: Increased overall circuit impedance
Force Output Degradation
When silencers become clogged, the effective pressure available for work decreases significantly:
| Silencer Condition | Available Pressure | Speed Impact | Force Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clean (0% blocked) | 100% | Baseline | Baseline |
| Partially clogged (25%) | 85% | -15% | -10% |
| Moderately clogged (50%) | 70% | -35% | -20% |
| Severely clogged (75%) | 45% | -55% | -35% |
Real-World Performance Data
Cylinder Response Characteristics
- Acceleration phase: Delayed start due to pressure buildup
- Constant speed: Reduced maximum velocity
- Deceleration: Erratic stopping with pressure spikes
- Dwell time: Extended cycle completion times
At Bepto, we’ve documented that our rodless cylinders maintain superior performance even with moderate silencer restriction compared to OEM alternatives, thanks to our optimized internal flow paths and precision-machined components that minimize pressure losses.
What Are the Warning Signs of Silencer Blockage in Pneumatic Systems?
Early detection prevents costly system failures and production downtime. 📊
Key warning signs include increased cycle times, irregular cylinder movement, excessive noise levels, visible contamination in exhaust ports, pressure gauge fluctuations, and abnormal heating of pneumatic components, particularly noticeable in high-frequency rodless cylinder applications where consistent exhaust flow is critical.
Primary Detection Methods
Visual Inspection Indicators
- Discolored silencers: Brown or black deposits indicate contamination
- Visible debris: Particles blocking exhaust ports
- Oil accumulation: Excessive lubrication buildup
- Corrosion signs: Rust or oxidation on metal components
Performance Monitoring
- Cycle time measurement: 10%+ increase indicates problems
- Pressure readings: Elevated exhaust back pressure
- Temperature checks: Hot components suggest restriction
- Sound analysis: Changed exhaust noise patterns
Diagnostic Checklist
| System Parameter | Normal Range | Warning Level | Critical Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cycle time variation | ±5% | ±15% | ±25% |
| Exhaust back pressure | <0.2 bar | 0.2-0.5 bar | >0.5 bar |
| Component temperature | Ambient +10°C | +20°C | +30°C |
| Noise level increase | <5 dB | 5-10 dB | >10 dB |
Remember Sarah, a production manager at a packaging facility in Manchester, UK? Her team noticed their rodless cylinder assembly line was running 20% slower than normal. After our technical assessment revealed 60% silencer blockage, we provided replacement Bepto silencers and restored full performance within hours, preventing a potential $15,000 daily production loss. 💪
How Can Clogged Silencers Damage Valves and Control Components?
Back pressure from blocked silencers creates destructive forces throughout the pneumatic circuit. ⚠️
Clogged silencers cause valve damage through pressure surges4, seat erosion, and thermal stress, while control components suffer from hunting behavior, reduced response time, and premature wear due to excessive back pressure that forces valves to work against restricted exhaust flow in rodless cylinder systems.
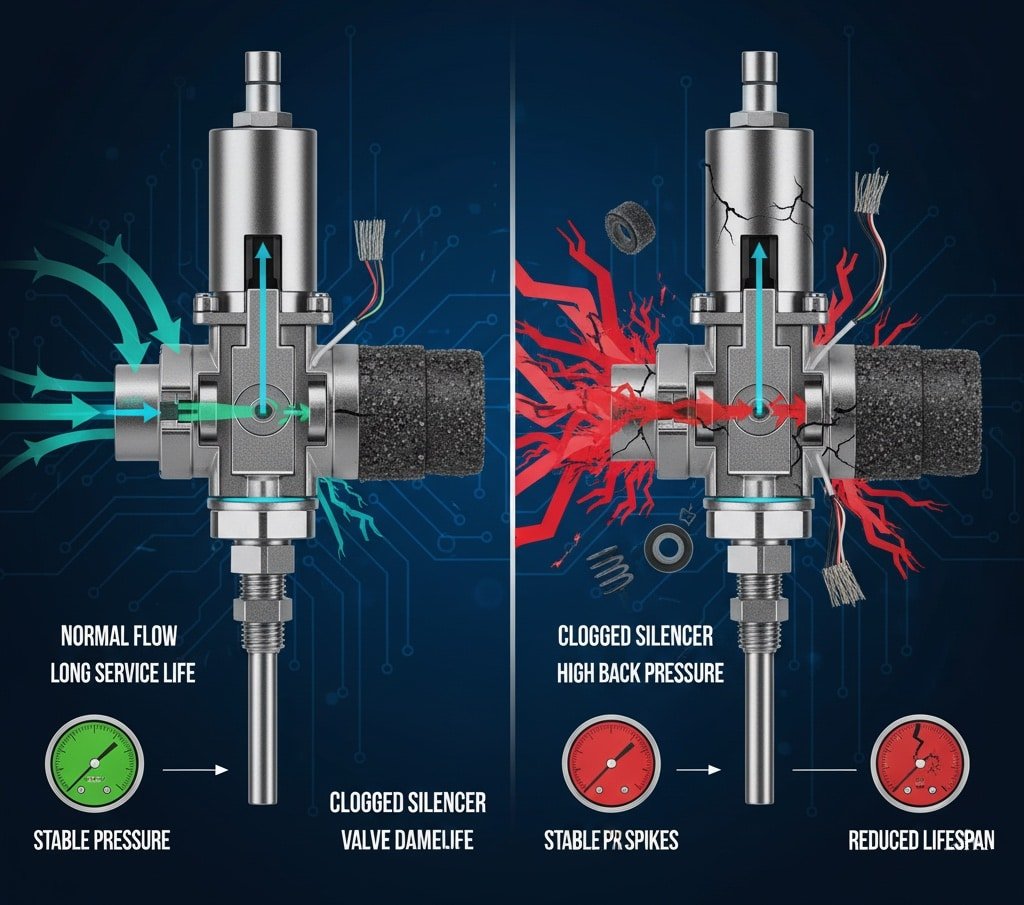
Valve Damage Mechanisms
Pressure-Related Failures
- Seat damage: High differential pressure causes erosion
- Spring fatigue: Constant pressure cycling weakens components
- Seal degradation: Excessive pressure accelerates wear
- Body cracking: Pressure spikes exceed design limits
Control System Impact
- Hunting behavior: Valves oscillate seeking stable position
- Response delays: Sluggish operation due to pressure buildup
- Accuracy loss: Reduced positioning precision
- Electrical stress: Solenoids work harder against back pressure
Component Comparison
| Component Type | Normal Life | With Clogged Silencers | Bepto Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Directional valves | 5-8 years | 2-3 years | Enhanced flow design |
| Pressure regulators | 3-5 years | 1-2 years | Superior materials |
| Flow controls | 4-6 years | 1.5-3 years | Precision manufacturing |
| Cylinder seals | 2-4 years | 6-18 months | Optimized seal grooves |
Prevention Strategies
System Design Considerations
- Adequate silencer sizing: 1.5x minimum flow requirement
- Multiple exhaust paths: Redundant flow routes
- Filtration upstream: Clean air reduces contamination
- Regular maintenance: Scheduled inspection intervals
Our Bepto pneumatic components feature enhanced exhaust flow designs that maintain performance even with moderate silencer restriction, providing built-in protection against common maintenance oversights.
What Maintenance Practices Prevent Silencer Clogging Issues?
Proactive maintenance eliminates costly performance degradation and component failures. 🛠️
Prevent silencer clogging through monthly visual inspections, quarterly cleaning with compressed air, semi-annual replacement of disposable elements, proper air filtration, and maintaining clean compressed air systems, especially critical for high-cycle rodless cylinder applications where consistent exhaust flow ensures optimal performance.
Maintenance Schedule
Weekly Tasks
- Visual inspection: Check for obvious contamination
- Performance monitoring: Record cycle times
- Pressure readings: Monitor system pressures
- Sound assessment: Listen for changes in exhaust noise
Monthly Maintenance
- Detailed inspection: Remove and examine silencers
- Cleaning procedure: Use clean, dry compressed air
- Component assessment: Check for wear or damage
- Documentation: Record findings and actions
Cleaning Procedures
Step-by-Step Process
- System shutdown: Depressurize completely
- Component removal: Carefully extract silencers
- Initial cleaning: Blow out loose debris
- Deep cleaning: Solvent wash if necessary
- Inspection: Check for damage or excessive wear
- Reassembly: Install with proper torque specifications
Replacement Guidelines
| Silencer Type | Service Life | Replacement Trigger | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sintered bronze | 12-18 months | 50% flow reduction | Medium |
| Plastic mesh | 6-12 months | Visible damage | Low |
| Paper element | 3-6 months | Discoloration | Low |
| Metal screen | 18-24 months | Corrosion signs | High |
Proper silencer maintenance is the most cost-effective way to ensure peak pneumatic system performance and maximize component life. 🚀
FAQs About Silencer Clogging
How often should pneumatic silencers be replaced in industrial applications?
Replace pneumatic silencers every 6-12 months in normal industrial environments, or when flow restriction exceeds 25% of original capacity. Harsh environments with high contamination may require monthly replacement. Our Bepto technical team provides application-specific maintenance schedules based on your operating conditions and cycle frequency.
Can I clean and reuse clogged pneumatic silencers?
Most sintered bronze and metal mesh silencers can be cleaned 2-3 times before replacement, while paper and plastic elements should be discarded when clogged. Use clean, dry compressed air and appropriate solvents for cleaning. However, replacement with new units often provides better long-term reliability and performance consistency.
What causes silencers to clog faster in some applications?
High contamination levels, excessive oil carry-over, dusty environments, and poor upstream filtration accelerate silencer clogging in pneumatic systems. Applications with frequent cycling, like rodless cylinder systems, may also experience faster accumulation due to higher air flow volumes. Proper air preparation significantly extends silencer service life.
How do I size silencers correctly to prevent performance issues?
Size silencers for 1.5-2 times the maximum flow rate of your pneumatic system to prevent restriction and ensure adequate safety margin. Undersized silencers create back pressure even when clean, while oversized units may not provide effective noise reduction. Our engineering team provides sizing calculations for optimal performance.
What’s the difference between cheap and quality silencers?
Quality silencers like our Bepto units feature superior materials, precise manufacturing tolerances, and optimized flow designs that maintain performance longer and resist clogging better than cheap alternatives. While initial cost may be higher, quality silencers provide lower total cost of ownership through extended service life and consistent performance.
-
Learn the definition of back pressure and how it impacts system efficiency. ↩
-
See a technical explanation of valve hunting and what causes this oscillation. ↩
-
Understand the principle of pressure differential and its role in creating fluid flow. ↩
-
Explore the causes and effects of pressure surges in pneumatic and hydraulic lines. ↩




